2022
Clinical Implications of Herbal Supplements in Conventional Medical Practice: A US Perspective
Herbal supplements are common complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) approaches with an ever-increasing use trend in the last two decades among the US population. Self-medication with herbal supplements which are promoted for general well-being, wei
www.cureus.com
Clinical Implications of Herbal Supplements in Conventional Medical Practice: A US Perspective
Table 3: Toxic herbs causing life-threatening side effects which warrant closer attention
| S.N. | Herb Name | Side Effects |
| 1 | Aristolochic Acid | nephrotoxic, carcinogenic |
| 2 | Chaparral | irreversible liver damage |
| 3 | Comfrey | hepatotoxic, carcinogenic, teratogenic |
| 4 | Ephedra/ma huang (ephedra sinica) | hypertension, myocardial infarction (MI), seizure, stroke, psychosis |
| 5 | Germander | hepatotoxic, death |
| 6 | Kava | hepatotoxic |
| 7 | Lobelia (Indian tobacco) | breathing problems, tachycardia, hypotension, coma, death |
| 8 | Magnolia-Stephania | kidney disease, permanent kidney failure |
| 9 | Willow bark | Reye’s syndrome in children, allergic reaction in adults |
| 10 | Wormwood | seizures, numbness of extremities, delirium, kidney failure |
| 11 | Yohimbe | BP irregularity, arrhythmia, kidney & neurologic disorders, death |
Table 6: List of published herbal supplements to be avoided during the perioperative period, pregnancy and breastfeeding
수술 전후, 임신 및 모유 수유 중 피해야 할 출판된 허브 보조제 목록
| Avoid When? | Herbal supplements to avoid | Reasons for avoiding the herbal supplements |
| Within two weeks of surgery [88,90] | Gingko biloba, Garlic, Ginseng, Dong Quai, Feverfew | Bleeding effects |
| Ephedra, Garlic | Cardiovascular effects: Ephedra (tachycardia, hypertension, and palpitations), Garlic (hypotension) | |
| Kava, Valerian root, SJW | Anesthetic effects | |
| Echinacea, Goldenseal, Licorice | Cytochrome P450 inhibitors (interacts with coumadin, cyclosporine, midazolam, oral contraceptives, testosterone, lidocaine, and digitalis) | |
| SJW | Cytochrome P450 inducers | |
| Kava, Valerian root | Effects on sedatives (benzodiazepine and barbiturates) | |
| SJW and Dong Quai | Photosensitivity | |
| Ginseng | Hypoglycemia | |
| During Pregnancy [91,92] | Ammi visnaga, Blue cohosh, Cat's Claw, Fenugreek, Feverfew, Pennyroyal, Sage, Thyme | Uterotonic effect causing preterm birth or abortion |
| Andrographis, Boldo, Catnip, Essential oils, Feverfew, Juniper, Licorice, Nettle, Red clover, Rosemary, Shepherd's purse, and Yarrow | Caution is needed during pregnancy due to safety concerns | |
| Dong Quai | Negatively affect the fetus | |
| Soy, Isoflavones, Red clover, Flaxseed, Lignans, and Hops | Estrogen-like properties with possible effects on the fetus | |
| Green tea | Theoretical concern for risk of birth defects due to effect on folate levels | |
| Traditional Chinese herbal combinations and Ayurvedic herbal combinations. | Associated toxic heavy metals, poisonous herbs, or unlabelled prescription drugs may damage the intrauterine growth or affect the lactating baby through milk | |
| During Breast Feeding [84,92] | Chasteberry | Milk-inhibiting potential |
| Aloe | Laxative effect due to anthraquinones glycosides excreted with breast milk | |
| Black Cohosh | Gastrointestinal irritation in baby | |
| Butterbur | Hepatotoxic effect due to pyrrolizidine alkaloids excreted with breast milk. | |
| Ephedra | Stimulants excreted in breast milk | |
| Goldenseal | May raise the infant bilirubin levels | |
| Kava Kava | CNS depressant due to pyrones in the breast milk | |
| Licorice root | Potential toxicity to the infant | |
| Senna leaf | Genotoxic anthraquinones excreted in breast milk | |
| Wormwood | Potential neurotoxins excreted in breast milk
Table 6: List of published herbal supplements to be avoided during the perioperative period, pregnancy and breastfeeding
|
Table 8: Summary of HDI, mechanisms, and outcomes
HDI, 메커니즘 및 결과 요약
GI: Gastrointestinal, H-D: Herb-Drug, AKA: also known as, P-gp: P-Glyco protein, MDR1: multi-drug resistance protein 1, MRP2: Multi-drug resistance-associated protein-2, BCRP: Breast cancer resistance protein, CYP: cytochrome P450, UGTs: Uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase
| Herb-Drug Interaction | Level of Interaction | Mechanism | Herbal Effect | Outcome |
| Pharmacokinetic (ADME) | Absorption (A) | efflux transporters (P-gp AKA MDR1, MRP2, BCRP) | inhibition/induction of efflux transporters located at the canalicular membrane of epithelium or endothelium | change in the blood concentration of the drug |
| GI motility | increase GI motility shortening the drug transit time and lowering absorption | |||
| insoluble H-D complex formation in GI tract | decrease drug bioavailability to a sub-therapeutic state | |||
| Distribution (D) | drug binding protein | displace protein-bound drugs increasing bioactive concentration | ||
| Metabolism (M) | CYP enzyme family (phase I) and non-CYP enzyme systems such as UGTs (phase II) | induction/inhibition of the metabolic enzymes in a competitive or non-competitive manner | ||
| Elimination (E) | renal (major) and biliary (minor) elimination of drugs | increase renal excretion of drugs and metabolites | ||
| Pharmacodynamic | Drug Target | simultaneous effects on the same drug sites/receptors | changes in the physiological effect and mechanism of action of the drug | additive, synergistic or antagonistic changes in the pharmacological effects of the drug |
Table 9: Free and subscription-based online HDI screening tools
무료 및 구독 기반 온라인 HDI 검사 도구
| HDI Screening | Interaction Checker | URL Link for Online Access | Platform Availability |
| Free tools | Drugs.com | https://www.drugs.com/drug_interactions.html | Web & App |
| Medscape | https://reference.medscape.com/drug-interactionchecker | Web & App | |
| WebMD | https://www.webmd.com/interaction-checker/default.htm | Web & App | |
| RxList | https://www.rxlist.com/drug-interaction-checker.htm | Web | |
| Merck Manual | https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/druginformation/drug-interactions | Web & App | |
| Subscription-based tools | Micromedex | https://www.micromedexsolutions.com/home/dispatch/ssl/true | Web & App |
| Lexicomp | https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/solutions/lexicomp/lexicomp | Web & App | |
| Facts and Comparisons | https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/solutions/lexicomp/facts-and-comparisons | Web | |
| PEPID | https://www.pepid.com/ | Web & App | |
| Natural Medicines | https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com/ | Web |
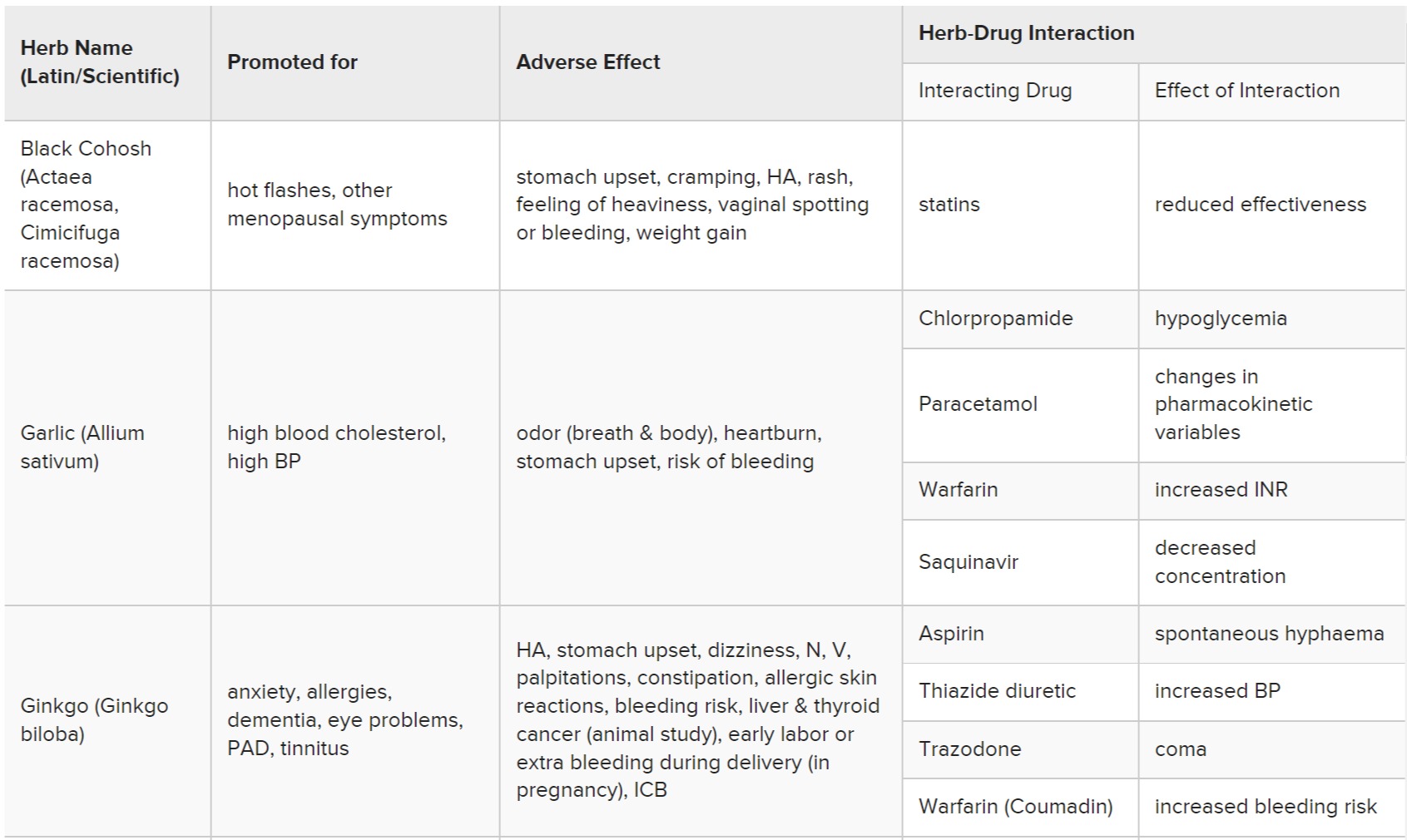
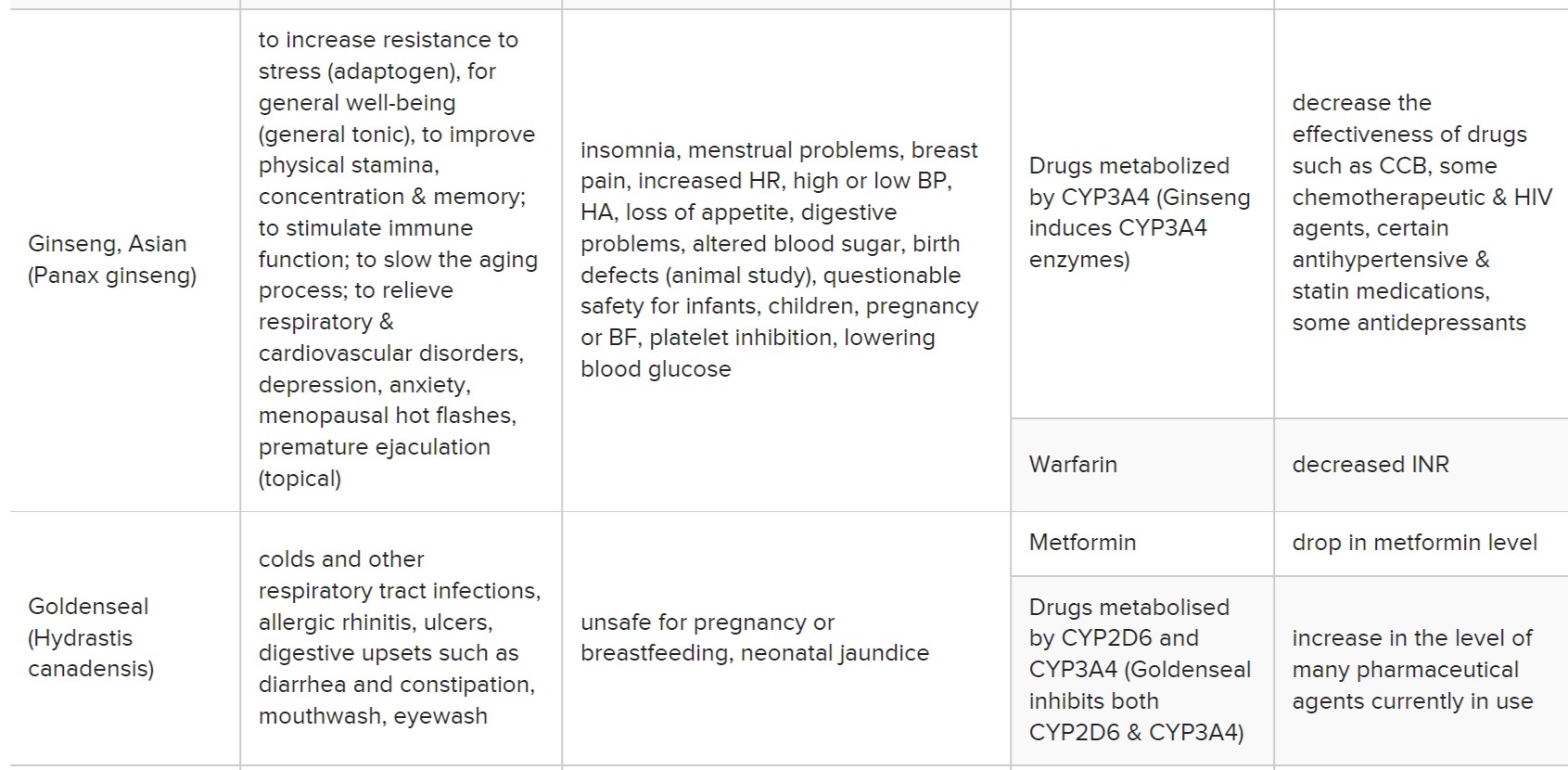
Table 10: Summary of adverse effects and herb-drug interactions of the most common herbs
가장 흔한 허브의 부작용 및 허브-약물 상호작용 요약
SJW: St. John’s Wort, INR: International Normalised Ratio, CYP: Cytochrome P-450 enzymes, P-gp: P-glycoprotein, BP: Blood Pressure, HR: Heart Rate, PAD: Peripheral Artery Disease, CCB: Calcium Channel Blockers, HA: Headache, N: nausea, V: vomiting, ADHD: attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, OCD: obsessive-compulsive disorder, GI: Gastrointestinal, ICB: intracerebral bleeding, BF: Breast Feeding, OC: Oral Contraceptives

2018
https://bjgp.org/content/68/675/e711
Prevalence of drug–herb and drug–supplement interactions in older adults: a cross-sectional survey
Background Polypharmacy is common among older adults, with increasing numbers also using prescription drugs with herbal medicinal products (HMPs) and dietary supplements. There is no reliable evidence from the UK on concurrent use of HMPs and dietary suppl
bjgp.org
Prevalence of drug–herb and drug–supplement interactions in older adults: a cross-sectional survey
Evaluation of potential interactions from HMPs, dietary supplements, and prescription drugs
HMP, 건강 보조 식품 및 처방약의 잠재적 상호 작용 평가
| HDI category: Significant hazard, dosage adjustment or close monitoring is needed | ||
| Bonecal (Pharmanutra) | Levothyroxine | The efficacy of levothyroxine has been reduced by calcium carbonate. Calcium acetate and calcium citrate reduced levothyroxine absorption in pharmacokinetic studies |
| Peppermint | Lansoprazole | Antacids may compromise the enteric coating of some commercially available peppermint oil capsules. H2-receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors may interact similarly |
| St John’s wort | Amlodipine | St John’s wort significantly reduces the bioavailability of verapamil. Other calcium channel blockers would be expected to interact similarly |
| HDI category: A potentially hazardous combination | ||
| Glucosamine | Metformin | In a controlled study, glucosamine supplements with chondroitin had no effect on glycaemic control in patients taking oral antidiabetic drugs, but increases in blood glucose concentrations have occurred in patients with treated and untreated diabetes |
| Omega 3 fish oil | Bisoprolol [2] | The hypotensive effect of propranolol might be enhanced by fish oils |
| Ginkgo | Rabeprazole | Ginkgo modestly reduces omeprazole levels. Most other proton pump inhibitors are likely to be similarly affected |
| HDI category: Doubt about outcome of concurrent usec | ||
| Omega 3 fish oil | Aspirin [2] | The concurrent use of aspirin and fish oils caused at least additive effects on bleeding time in healthy subjects, but clinical studies in patients taking aspirin alone and with clopidogrel have found no evidence of an increase in incidence of bleeding episodes |
| Cod liver oil | Aspirin [2] | The concurrent use of aspirin and fish oils caused at least additive effects on bleeding time in healthy subjects, but clinical studies in patients taking aspirin alone and with clopidogrel have found no evidence of an increase in incidence of bleeding episodes |
| Cod liver oil | Bisoprolol Propranolol |
The hypotensive effect of propranolol might be enhanced by fish oils |
| Flaxseed | Rivaroxaban | Limited evidence suggests that flaxseed oil may have some antiplatelet effects, which could be additive with those of conventional antiplatelet drugs, and increase the risk of bleeding with anticoagulants |
| Green tea | Lisinopril | Both black and green tea might cause a modest increase in blood pressure, which might be detrimental to the treatment of hypertension. Green tea reduced the effects of nadolol on blood pressure in healthy subjects |
| Senna pods | Indapamide | Theoretically, patients taking potassium-depleting diuretics could experience excessive potassium loss if they also regularly use, or abuse, anthraquinone-containing substances such as senna |
| Glucosamine | Co-codamol Paracetamol |
Limited evidence suggests that glucosamine might reduce the efficacy of paracetamol (acetaminophen) |
| Glucosamine | Furosemide Bendroflumethiazide [2] |
Limited evidence from a large open study suggests that unnamed diuretics might slightly reduce the efficacy of glucosamine to some extent |
| Echinacea | Midazolam | Echinacea does not appear to alter the AUC and clearance of oral midazolam, although the bioavailability may be increased. Clearance of intravenous midazolam may be modestly increased in patients taking Echinacea |
| Hawthorn | Nifedipine | Limited evidence suggests that there may be additive blood pressure-lowering effects if hawthorn is taken with conventional antihypertensives, but the effects are small |
| Visionace® (Vitabiotics) (lutein, carotenoids, myrtillus, flavonoid compounds) | Lansoprazole | The desired effect of betacarotene supplementation may be reduced in those taking proton pump inhibitors |
| Evening primrose oil | Aspirin | Evening primrose oil can inhibit platelet aggregation and increase bleeding time. It has therefore been suggested that it may have additive effects with other antiplatelet drugs, but evidence of this is generally lacking |
- ↵a The number of patients exposed to the particular combination of HMPs/dietary supplement and prescription drug.
- ↵b Potential interaction reports from Stockley’s Herbal Medicines Interactions.
- ↵c Guidance about possible adverse effects and/or some monitoring may be needed.
- a HMP/식이 보조제 및 처방약의 특정 조합에 노출된 환자 수.
- ↵b Stockley's Herbal Medicines Interactions의 잠재적 상호작용 보고서.
- ↵c 가능한 부작용 및/또는 일부 모니터링에 대한 지침이 필요할 수 있습니다.AUC = area under the curve. HDI = herb–drug interaction. HMP = herbal medicinal product.
The HMPs implicated in the potential risk for interaction include:
- flaxseed;
- evening primrose oil;
- St John’s wort;
- peppermint;
- senna;
- Echinacea;
- hawthorn;
- green tea; and
- ginkgo.
The five dietary supplements implicated are:
- glucosamine;
- cod liver oil;
- omega 3 fish oil;
- calcium carbonate; and
- a multivitamin.
확인된 상호작용의 대부분은 칼슘 채널 차단제, HMG-CoA 환원효소 억제제(스타틴), 아스피린을 포함한 처방약의 농도 또는 효과의 잠재적인 변경과 관련이 있습니다. 위험한 결과를 초래할 가능성이 있는 것으로 평가된 7가지 허브-약물 및 보조제-약물 상호 작용은 혈당 농도 증가, 출혈 위험, 처방약의 효능 또는 생체 이용률 감소와 관련이 있습니다.
*********************************************************************************
2022
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-17704-z
Herb-anticancer drug interactions in real life based on VigiBase, the WHO global database
Green tea—Camelia sinensis (L.) Kuntze
Cannabis—Cannabis sativa L.
Table 2 (A) Camellia sinensis L. & (B) Cannabis sativa L.- ACD interactions among selected ICSRs.
From: Herb-anticancer drug interactions in real life based on VigiBase, the WHO global database
| OACD Drug | ||||||||
| Erlotinib/CSa1/Squamous cell carcinoma | SmPc | Subst9 | Pgp | Inh/down-regulation of Pgp expression10,11,12,13 | EGCG | PK: ↑ cutaneous rash | * | C-2 |
| Erlotinib/CSa2/Non-small cell lung cancer | SmPc | Subst9 | Pgp | Inh/down-regulation of Pgp expression10,11,12,13 | EGCG | PK: ↑ dyspnea, hemoptysis |
** | C-2 |
| Imatinib/CSa3/Unknown | SmPc | Anemia9 | Digestive iron absorption | ↓ absorption of iron14 | Catechins | PD: ↑ anemia | * | C-3 |
| Anastrazole/Csa4/breast cancer recurrent | SmPc | Common hepatic side-effects | Liver | Hepatotoxicity15 | EGCG | PD: ↑hepatocellular injury, cholestasis | * | D-2 |
| PACD Drug | ||||||||
| Methotrexate/CSa5/Localized osteosarcoma | In vitro/in vivo | Subst16,17,18 | OATP-A/B and AOX | Inh19 | EGCG | PK: ↑ hepatotoxicity | * | C-2 |
| OACD Drug | ||||||||
| Everolimus/CSb1/Unknown | SmPc | Subst9 | CYP3A4; Pgp | CYP3A4 subst26,35/inh27 Pgp inh29,35,36 |
THC + metabolites 11-OH-THC and CBD | PK: ↑ nausea | ** | B-3 |
| Nintedanib/CSb2/Unknown | SmPc | Subst9 | Pgp | Inh29,35,36 | CBD | PK: ↑ Hepatic enzymes | ** | C-0 |
| Palbociclib/CSb3/Unknown | SmPc | Subst9,37 | CYP3A4; Pgp | CYP3A4 subst26,35/inh27 Pgp inh29,35,36 |
THC + metabolites 11-OH-THC and CBD | PK: ↑ Tumour marker + Malaise | ** | E-3 |
| PACD Drug | ||||||||
| Carfilzomib/CSb4/Unknown | Case report | Dyspnea & cough33,34 | CNS | respiratory distress syndrome30,31,32 | n. k. | PD: ↑ chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | * | C-2 |
Black cohosh—Cimicifuga racemosa (L.) Nutt.
Turmeric—Curcuma longa L.
Table 3 (A) Cimicifuga racemosa L. & (B) Curcuma longa L.—ACD interactions among selected ICSRs.
From: Herb-anticancer drug interactions in real life based on VigiBase, the WHO global database
| OACD Drug | ||||||||
| Fingolimob/CR1/Unknown | SmPC | Subst (+ Ind)9 | CYP3A4 & Liver | weak inh43 & hepatotoxicity42 | Triterpene glycosides (CYP3A4 inhibition) | PK/PD: ↑ hepatic damage, liver cholestasis, jaundice, epigastralgy, nausea, ↓ appetite | * | D-2 |
| PACD Drug | ||||||||
| Trastuzumab+ Pertuzumab/CR2/Hepatic mestastasis | SmPC | Common hepatic side effect9 | Liver | Hepatotoxicity42 | n.k. | PD: ↑ hepatic damages @↓ appetite | * | D-2 |
| OACD Drug | ||||||||
| Everolimus + Sunitinib/CL1/Pancreatic carcinoma | SmPC | Subst (Everolimus)8 | CYP3A4/Pgp | Inh CYP3A439/Pgp40 | Curcumin | PK: ↑ Blood triglycerides increased, pain in jaw, dry skin | * | C-0 |
| Ruxolitinib/CL2/Unknown | SmPC | Subst8 | CYP3A4 | Inh of CYP3A439 | Curcuminoids | PK: ↑ myalgia, fatigue, hemoglobin | * | C-0 |
| Ibrutinib/CL3/Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | SmPC | Subst8 | CYP3A4 | Inh39 | Curcuminoids | PK: ↑ thrombocytopenia, neutropenia | * | C-0 |
| Ibrutinib/CL4/Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | SmPC | Subst8 | CYP3A4 | Inh39 | Curcuminoids | PK: ↑ nausea, hypertension, hemorrhage, stomatitis, onychoclasis | * | C-0 |
| Ibrutinib/CL5/Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | SmPC | Subst8 | CYP3A4 | Inh39 | Curcumin | PK: ↑ dysgeusia, nausea, hypertension, hemorrhage, stomatitis, onychoclasis d | * | C-0 |
| Methotrexate/CL6/Unknown | SmPC | Increased hepatic enzymes in blood8 | Liver | Hepatotoxicity41 | Curcuminoids | PD: ↑ hepatoxicity | ** | D-2 |
| Palbociclib/CL7/Breast carcinoma | SmPC | Subst39 | CYP3A4 | Inh39 | Curcuminoids | PK: ↑ Hematotoxicity | * | C-0 |
| PACD Drug | ||||||||
| Bortezomib/CL8/Pasma cell myeloma | HUG | Subst4 | CYP3A4 | Inh47 | Curcuminoids | PK: ↑ Constipation@Red blood cell count decreased@Night sweats@Neuropathy peripheral@Rash macular | * | C-2 |
St John’s wort—Hypericum perforatum L.
Table 4 Hypericum perforatum L.- ACD interactions among selected ICSRs.
From: Herb-anticancer drug interactions in real life based on VigiBase, the WHO global database
| OACD Drug | ||||||||
| Everolimus/HP1 /Myelodysplastic syndrome | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4/Pgp | CYP3A4 ind & Pgp inh4 | Hyperforin | PK: ↓ drug blood level | ** | E-4 |
| Nilotinib/HP2/ hronic myeloid leukemia | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | CYP3A4 ind4 | Hyperforin | PK: ↓ drug blood level | ** | E-4 |
| PACD Drug | ||||||||
| Temozolomide/HP3/Unknown | SmPC | Photosensitivity58 | cutaneous | Photosensitvity58 | Hypericin | PD: Radiation induced optic neuropathy | ** | D-3 |
Milk thistle—Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn.
Table 5 Silybum marianum L.- ACD interactions among selected ICSRs.
From: Herb-anticancer drug interactions in real life based on VigiBase, the WHO global database
| OACD Drug | ||||||||
| Gefitinib/SM1/Unknown | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | Inh60,61 downregulate 62 | Silymarin | PK: ↑ pruritus | ** | C-4 |
| Gefitinib/SM2/Unknown | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | Inh60,61 downregulate 62 | Silymarin | PK: ↑ mouth dryness | * | B-4 |
| Gefitinib/SM3/Unknown | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | Inh60,61 downregulate 62 | Silymarin | PK: ↑ somnolence | * | B-4 |
| Gefitinib/SM4/Unknown | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | Inh60,61 downregulate 62 | Silymarin | PK: ↑ nausea, cutaneous cracks | * | B-4 |
| Gefitinib/SM5/Unknown | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | Inh60,61 downregulate 62 | Silymarin | PK: ↑ prurit | * | B-4 |
| Sorafenib/SM6/Unknown | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | Inh60,61 downregulate 62 | Silymarin | PK: ↑ diarrhea | ** | B-4 |
| Sorafenib/SM7/Unknown | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | Inh60,61 downregulate 62 | Silymarin | PK: ↑ alopecia | * | D-4 |
| Sorafenib/SM8/Unknown | In vitro | Subst68 | OATP 1B1/3 | Inh63,64 | Silymarin | PK: ↑nail discoloration | ** | D-2 |
| Imatinib/SM9/Leukemia | HUG | Subst4 | CYP2C9 | Inh66,67 | Silymarin/silibinin | PK: ↑ anemia, pyrexia | * | D-4 |
| Capecitabine/SM10/Unknown | HUG | Subst4 | CYP2C9 | Inh66,67 | Silymarin/silibinin | PK: ↑ pruritus | ** | B-4 |
| Capecitabine/SM11/Unknown | HUG | Subst4 | CYP2C9 | Inh66,67 | Silymarin/silibinin | PK: ↑ nausea | ** | B-4 |
| PACD Drug | ||||||||
| Methotrexate + Vincristine/ SM12/Unknown | In vitro/in vivo | Vincr: CYP3A4 & Pgp subst4; MTX: OATP subst63 | CYP3A4/OATP-B1 | Inh CYP3A460,61 downregulate62 Inh OATP69 | Silymarin/silibinin | PK: ↑ abdominal pain | * | B-2 |
| Doxorubicine/SM13/Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | Inh60,61 downregulate62 | Silymarin | PK: ↑ arrhythmia | * | C-4 |
Mistletoe—Viscum album
Table 6 (A) Viscum album L. & (B) Zingiber officinale Roscoe—ACD interactions among selected ICSRs.
From: Herb-anticancer drug interactions in real life based on VigiBase, the WHO global database
| A - OACD Drug | Target | Viscum album L. | Clinic | |||||
| Anastrazole/ VA13/Unknown | SmPC | Rash9 | cutaneous | Rash 77 | Helixor M | PD: ↑ urticaria | * | B-3 |
| A - PACD Drug | Target | Herb | Clinic | |||||
| Cisplatin/ VA1/Malignant neoplasm of cervix uteri | SmPC | Neutropenia9 | Neutrophil | Neutropenia78 | Abnovaviscum M 2 mg | PD: ↑ neutropenia | ** | C-4 |
| Oxaliplatin + fluorouracil/ VA2/Malignant neoplasm of bladder | SmPC | Neutropenia9 | Neutrophil | Neutropenia78 | Abnovaviscum M 0.02 mg | PD: ↑ febril neutropenia | ** | C-4 |
| Cisplatin + fluorouracil/ VA3/Malignant neoplasm | SmPC | Thrombopenia9 | Thrombocyte | Thrombopenia83 | Abnovaviscum F 20 mg | PD: ↑ thrombocytopenia | ** | C-4 |
| Carboplatin + paclitaxel/ VA4/Malignant neoplasm of ovari | SmPC | Leucopenia9 | Leucocyte | Leucopenia78 | Abnovaviscum M 2 mg | PD: ↑ leucopenia | ** | C-4 |
| Carboplatin + paclitaxel/ VA5/Malignant neoplasm | SmPC | Neutropenia9 | Neutrophil | Neutropenia78 | Abnovaviscum F 2mg | PD: ↑ neutropenia | ** | C-4 |
| Paclitaxel/ VA6/Malignant neoplasm | SmPC | Neutropenia9 | Neutrophil | Neutropenia78 | Abnovaviscum F 2mg | PD: ↑ neutropenia | ** | C-4 |
| Cisplatin + paclitaxel/ VA7/Malignant neoplasm of pyloric antrum | SmPC | Nausea9 | Gastrointestinal disorders /cutaneous | Nausea78 | Abnovaviscum M 20 mg | PD: ↑ nausea, rash, hot flush | ** | B-3 |
| Trastuzumab/ VA8/Breast cancer recurrent | SmPC | Nausea9 | Gastrointestinal disorders | Nausea78 | Iscador M | PD: ↑ nausea | ** | B-3 |
| Ifosfamide/ VA9/Malignant neoplasm of breast | SmPC | Nausea9 | Gastrointestinal disorders | Nausea78 | Abnovaviscum F 20 mg | PD: ↑ nausea | ** | B-3 |
| Topotecan/ VA10/Unknown | SmPC | Urticaria9 | cutaneous | Urticaria78 | Helixor A 100 mg | PD: ↑ urticaria | ** | B-3 |
| Cisplatin + fluorouracil/ VA11/Unknown | SmPC | Syncope9 | Vascular/general disorders | Syncope83 | Helixor A | PD: ↑ syncope | ** | C-4 |
| Epirubucine/ VA12/Breast cancer | SmPC | Fever9 | General disorders | Pyrexia83 | ? | PD: ↑ fever | ** | B-4 |
| B - OACD Drug | Target | Zingiber officinale Roscoe | Clinic | |||||
| Imatinib/ZO1/Chronic myeloid leukemia | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 | Inh85,86 | Gingerols | PK: ↑ hepatotoxicity | ** | C-0 |
| Dabrafenib/Trametinib/ZO2/Metastatic melanoma | SmPC | Subst9 (minor for Trametinib) | CYP3A4/Pgp | Inh85,86 | Gingerols | PK: ↑ thrombocytopeniarectal hemorrhage | * | C-0 |
| Crizotinib/ZO3/Adenocarcinoma of lung | SmPC | Subst9 | CYP3A4 & Pgp | Inh85,86 | Gingerols | PK: ↑ hepatic impairment | * | C-2 |
*************************************************************************************
2018
https://www.cancernetwork.com/view/herb-drug-interactions-cancer-care
Herb-Drug Interactions in Cancer Care
In this article, we describe the mechanisms via which interactions between herbs and prescription drugs may occur, and highlight four popular herbs and a medicinal mushroom commonly used by cancer patients, along with reports of their interactions with sta
www.cancernetwork.com
Herb-Drug Interactions in Cancer Care
일반적인 허브와 잠재적 상호 작용
심황Turmeric
전통 의학에서는 순환과 소화를 개선하는 데 자주 사용됩니다.
심황 추출물은 관절염 및 암 예방을 위한 식이 보조제로 판매됩니다.
활성 성분은 광범위하게 연구된 커큐민입니다.
예비 데이터에 따르면 커큐민은 암 치료로 인한 부작용을 완화하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
경구용 커큐민은 또한 결장직장암 환자의 악액질과 전반적인 건강을 개선했습니다..
진행성 췌장암 환자 21명을 대상으로 한 2상 시험에서 curcumin은 핵인자 αB 및 cyclooxygenase-2를 하향 조절하여 생체 활성을 시연했습니다.
제한된 흡수에도 불구하고, 2명의 환자에서 항종양 반응이 나타났다.
커큐민은 안전한 것으로 보고되었지만 항산화 특성으로 인해 사이클로포스파미드 및 독소루비신과 같은 화학 요법 약물과 상호 작용할 수 있습니다.
또한 CYP450 효소를 방해하는 것으로 알려져 있으며 기질 약물과 상호 작용할 수 있습니다.
또한 항혈소판 특성 때문에 커큐민은 항응고제와 함께 사용할 때 출혈 위험을 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
녹차
녹차와 그 추출물은 고지혈증, 고혈압, 죽상동맥경화증 및 암을 예방하고 치료하는 데 사용되었습니다.
녹차 추출물의 활성 성분은 에피갈로카테킨-3-갈레이트(EGCG)입니다.
녹차 추출물은 전암성 용종 형성을 방지하고 유방암 세포의 증식을 억제하며 방광암 세포의 세포자멸사를 유도함으로써 화학 예방 활성을 입증했습니다
전임상 연구에 따르면 녹차의 폴리페놀 성분이 항암제인 보르테조밉의 치료 효과를 무효화하는 동시에 타목시펜 및 이리노테칸과 함께 사용할 경우 독성 위험을 증가시킬 수 있음이 나타났습니다.
간독성 위험도 증가했습니다.
아세트아미노펜과 함께 사용하거나 공복에 섭취할 때 보고되었습니다.[45,46]
임상 연구에 따르면 800mg의 EGCG를 복용하면 간 효소 상승과 관련이 있으며, 이는 섭취 중단 후 가역적이었습니다.
관찰 연구에 따르면 폐경 후 여성의 경우 섭취가 유방암 위험을 높일 수 있습니다.
녹차의 일일 소비량은 1~3잔으로 다양했습니다. 위험은 차를 마시기 시작한 연령에 따라 수정되는 것으로 보이며, 20세 이전에 시작한 여성에게는 보호 효과가 있고 50세 이후에 시작한 여성에게는 위험이 증가합니다.녹차 추출물은 CYP450 3A4 효소를 방해하는 것으로 알려져 있으며 이 효소에 의해 대사되는 약물의 세포 내 농도에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
생강Ginger
Zingiber officinale 식물의 뿌리줄기인 생강 은 아시아와 아랍 전통에서 감기, 두통, 발열, 위장병 및 염증성 질환을 치료하기 위해 오랫동안 요리 향신료와 약재로 사용되어 왔습니다.
임상 시험에 따르면 생강은 임신, 멀미, 수술 후 메스꺼움과 구토를 효과적으로 감소시킬 수 있습니다.
화학 요법으로 인한 메스꺼움을 예방하는 효능에 대한 연구 결과도 유망합니다.
그러나 무작위, 통제 및 교차 시험에서는 데이터가 임상 사용을 권장하는 데 결정적이지 않다는 것을 발견했습니다.
종단 연구에 따르면 와파린을 투여받는 환자에서 생강을 병용하면 출혈 위험이 높아집니다(교차비, 3.20, 95% CI, 2.42–4.24).
일반적인 경고는 출혈 증가의 잠재적 위험으로 인해 수술 전후 환경에서 생강 보충제 사용을 중단하는 것입니다.
최근의 체계적인 검토에 따르면 생강의 혈소판 응집 및 응고 특성에 대한 결과는 모호합니다.
아슈와간다Ashwagandha
Ayurveda에서 의약 효과로 높이 평가되는 관목인 ashwagandha( Withania somnifera )는 스트레스, 불안 및 피로를 완화, 골관절염 및 피부 질환 치료; 젊어지게 하다; 그리고 지구력을 향상시키기 위해하는 데 사용됩니다.
불안 완화제로 널리 홍보되고 있습니다.
활성 성분에는 알칼로이드, 사포닌 및 비타놀라이드로 알려진 스테로이드성 락톤이 포함됩니다.
임상 연구는 불안 완화에 유용성을 보여줍니다.
무릎 관절 통증이 있는 환자의 진통, 항염 및 연골 보호 효과 생성; 유방암 환자에 대한 소규모 연구에서 삶의 질 향상과 함께 화학 요법으로 인한 피로를 완화하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
일반적으로 안전한 것으로 간주되지만 ashwagandha는 트리아졸람의 진정 효과를 강화하는 것으로 보고되었습니다.
영지버섯Reishi mushroom
식물은 아니지만 영지버섯( Ganoderma lucidum )은 암 환자들이 흔히 사용하는 약용 버섯입니다.
그것은 아시아의 전통적인 의료 시스템의 중요한 구성 요소이며 신체를 강화하고 활력을 높이며 불면증을 치료하는 데 사용됩니다.
예비 데이터에 따르면 영지는 진행성 암 환자의 면역 반응을 향상시키는 데 효과적입니다.
간세포 암종의 관해도 몇몇 사례에서 보고되었습니다.
자실체의 추출물과 포자는 암에 대한 임상 시험에 사용되었습니다.
그럼에도 불구하고 전임상 연구에서 그 사용에 대한 우려가 제기되었습니다.
영지는 항혈소판 효과 때문에 항응고제/항혈소판제와 함께 사용할 때 출혈 위험을 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
또한 항산화 특성으로 인해 일부 화학 요법제의 효과를 잠재적으로 감소시킬 수 있습니다.
또한 면역 반응을 변경할 수 있습니다.
또한 영지는 CYP450 효소를 억제하고 기질 약물의 독성을 증가시킬 수 있다고 보고되었습니다.
허브 제품을 홍보하는 상업 웹사이트에서 잠재적인 부작용이나 상호작용에 대한 정보는 종종 최소화되거나 무시됩니다.
이 문제를 해결하기 위해 Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center의 통합 의학 서비스는 "약초에 대하여" 웹사이트를 개발했습니다: www.mskcc.org/aboutherbs.
여기에는 암 환자들이 사용하는 280가지 이상의 건강 보조 식품 및 가짜 치료법에 대한 객관적인 정보가 포함되어 있습니다.
이러한 제품의 효과와 잠재적으로 상호 작용할 수 있는 약물의 작용 메커니즘이 나열되어 있습니다.
의료 전문가 버전과 소비자 버전이 모두 있는 이 수상 경력에 빛나는 사이트는 임상의와 환자에게 무료로 제공됩니다.
신뢰할 수 있는 정보를 제공하는 기타 데이터베이스에는 무료로 액세스할 수 있는 National Institutes of Health's Office of Dietary Supplements ( https://ods.od.nih.gov ), ConsumerLab.com 및 Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database ( www.naturaldatabase .com ), 둘 다 서비스 요금을 부과합니다.
**********************************************************************************
2013
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/18/5/5125/htm
Herb-Herb Combination for Therapeutic Enhancement and Advancement: Theory, Practice and Future Perspectives
Herb-herb combinations have been used in Chinese medicine practice for thousands of years, yet scientific evidence of their therapeutic benefits is lacking. With increasing interest in shifting from the one-drug-one-target paradigm to combination therapy o
www.mdpi.com
Herb-Herb Combination for Therapeutic Enhancement and Advancement: Theory, Practice and Future Perspectives
***************************************************************************************
https://blog.naver.com/yoonbokc1/221577637248
암치료에 대한 새로운 패러다임, 식사와 영양에 의한 암의 치료가능성의 탐색(업데이트 중인 글
Cancer Prevention and Treatment by Wholistic Nutrition.[4] 전체적인 영양학에 의한 암의 예방과 ...
blog.naver.com
'약물' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 허브의 임상 효능, 부작용 및 약물 상호 작용 평가에 대한 중요한 접근 방식 (0) | 2022.10.09 |
|---|---|
| 건강 보조 식품 및 한약 독성 - 예측 시기 및 관리 방법 (0) | 2022.10.09 |
| black seed 오일의 thymoquinone (0) | 2022.10.03 |
| 요오드 와 암 (0) | 2022.10.01 |
| Herb–drug interactions (표) (0) | 2022.10.01 |