An Alternative Pipeline for Glioblastoma Therapeutics: A Systematic Review of Drug Repurposing in Glioblastoma
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/13/8/1953/htm
An Alternative Pipeline for Glioblastoma Therapeutics: A Systematic Review of Drug Repurposing in Glioblastoma
The treatment of glioblastoma (GBM) remains a significant challenge, with outcome for most pa-tients remaining poor. Although novel therapies have been developed, several obstacles restrict the incentive of drug developers to continue these efforts includi
www.mdpi.com
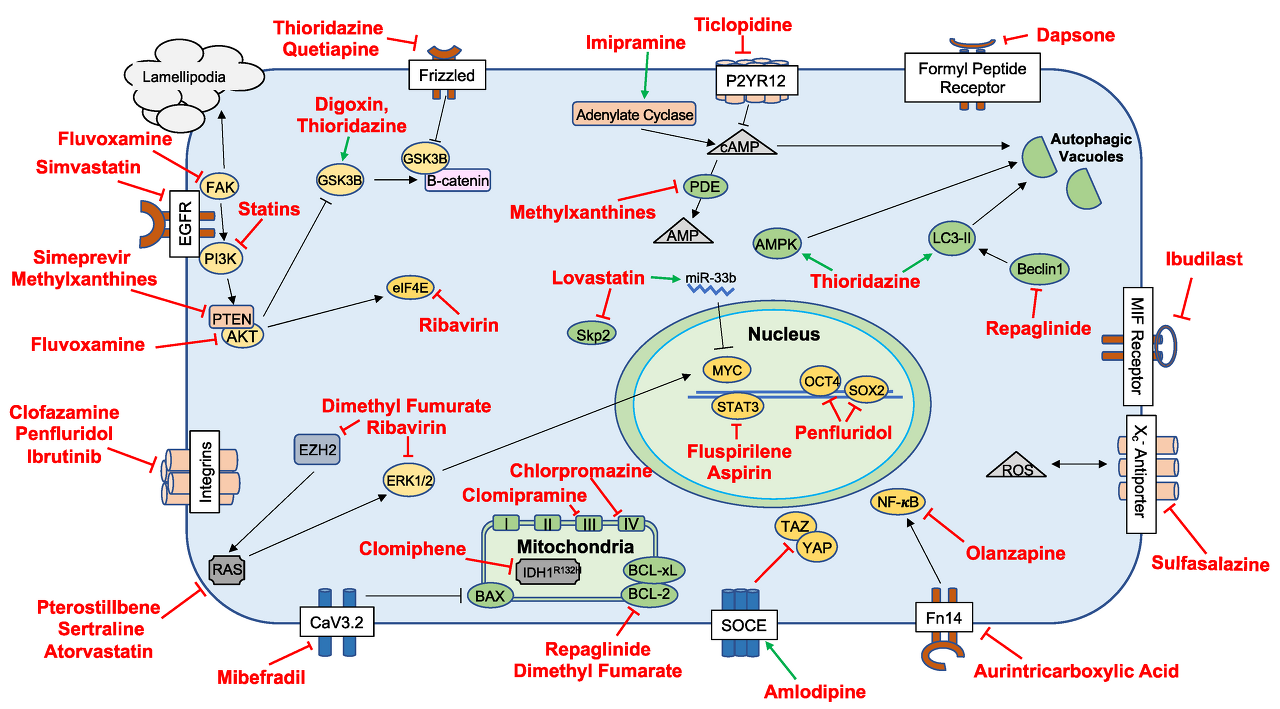
전임상 조사를 완료했지만 임상 환경에서 아직 완전히 연구되지 않은 약물의 주요 제안 메커니즘을 자세히 설명하는 세포 경로 및 상호 작용
Abbreviations: Adenosine diphosphate receptor (P2YR12); cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP); adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (AMP); phosphodiesterase (PDE); glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3B); phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K); AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK); microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate (LC3-II); signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3); (sex determining region Y)-box 2 (SOX2); octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (OCT4); focal adhesion kinase (FAK); phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN); protein kinase B (AKT); eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF4e); S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2); microRNA-33b (miRNA-33b); Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF); reactive oxygen species (ROS); tafazzin (TAZ); yes associated protein (YAP); fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14); store-operated calcium entry (SOCE); isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1); enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2); rat sarcoma (RAS); extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK); epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); t-type calcium channel (CaV3.2); Bcl-2-associated X protein (BAX); B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2); B-cell lymphoma-xL (BCL-XL); nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-KB).
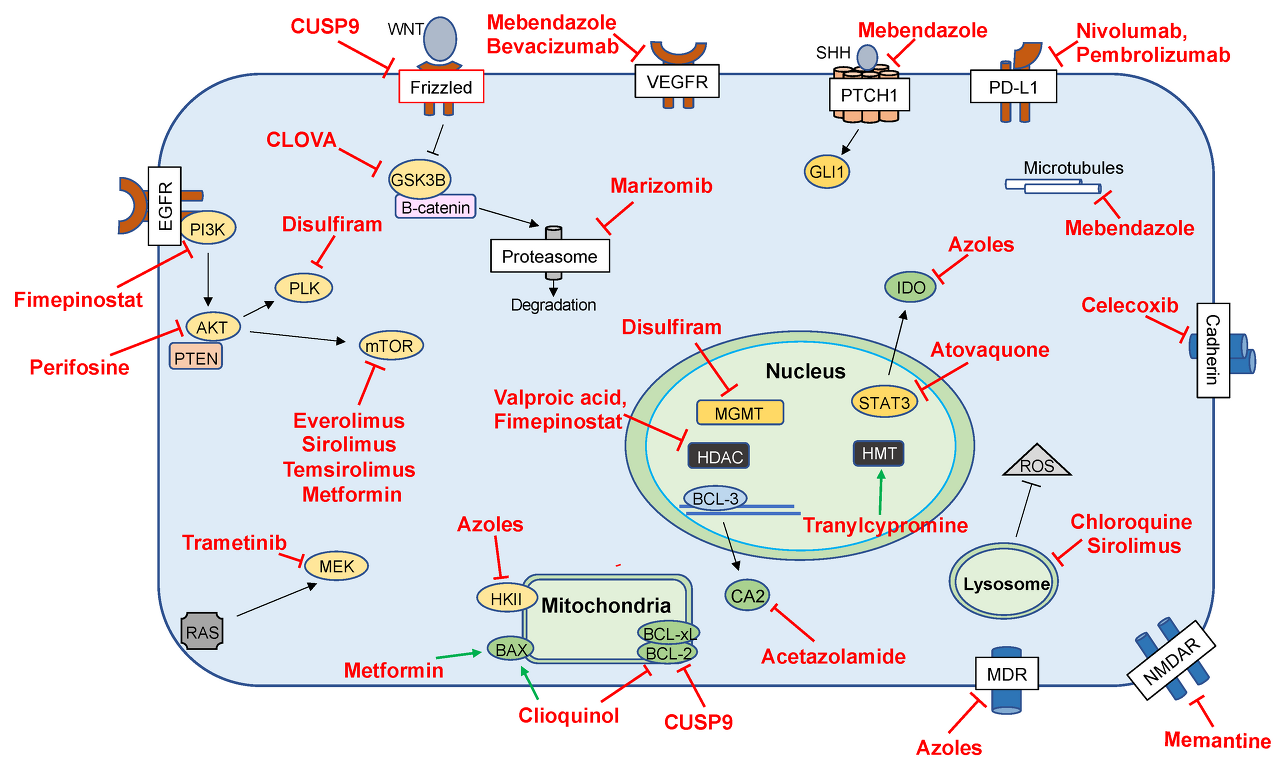
그림 2. 전임상 조사를 완료하고 임상에서도 연구된 약물의 주요 제안 메커니즘을 자세히 설명하는 세포 경로 및 상호 작용
Abbreviations: Histone deacetylase (HDAC); O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT); histone methyltransferase (HMT); carbonic anhydrase 2 (CA2); muli-drug resistance protein (MDR); N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR); Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO); glioma-associated oncogene (GLI1); protein patched homolog 1 (PTCH1); programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1); polo-like kinase 1 (PLK); mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK); mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR); hexokinase II (HKII); glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3B); phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K); signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3); phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN); protein kinase B (AKT); reactive oxygen species (ROS); rat sarcoma (RAS); extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK); vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR); endothelial growth factor receptor (EGFR); Bcl-2-associated X protein (BAX); B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2); B-cell lymphoma-xL (BCL-XL): B-cell lymphoma 3-encoded protein (BCL-3).
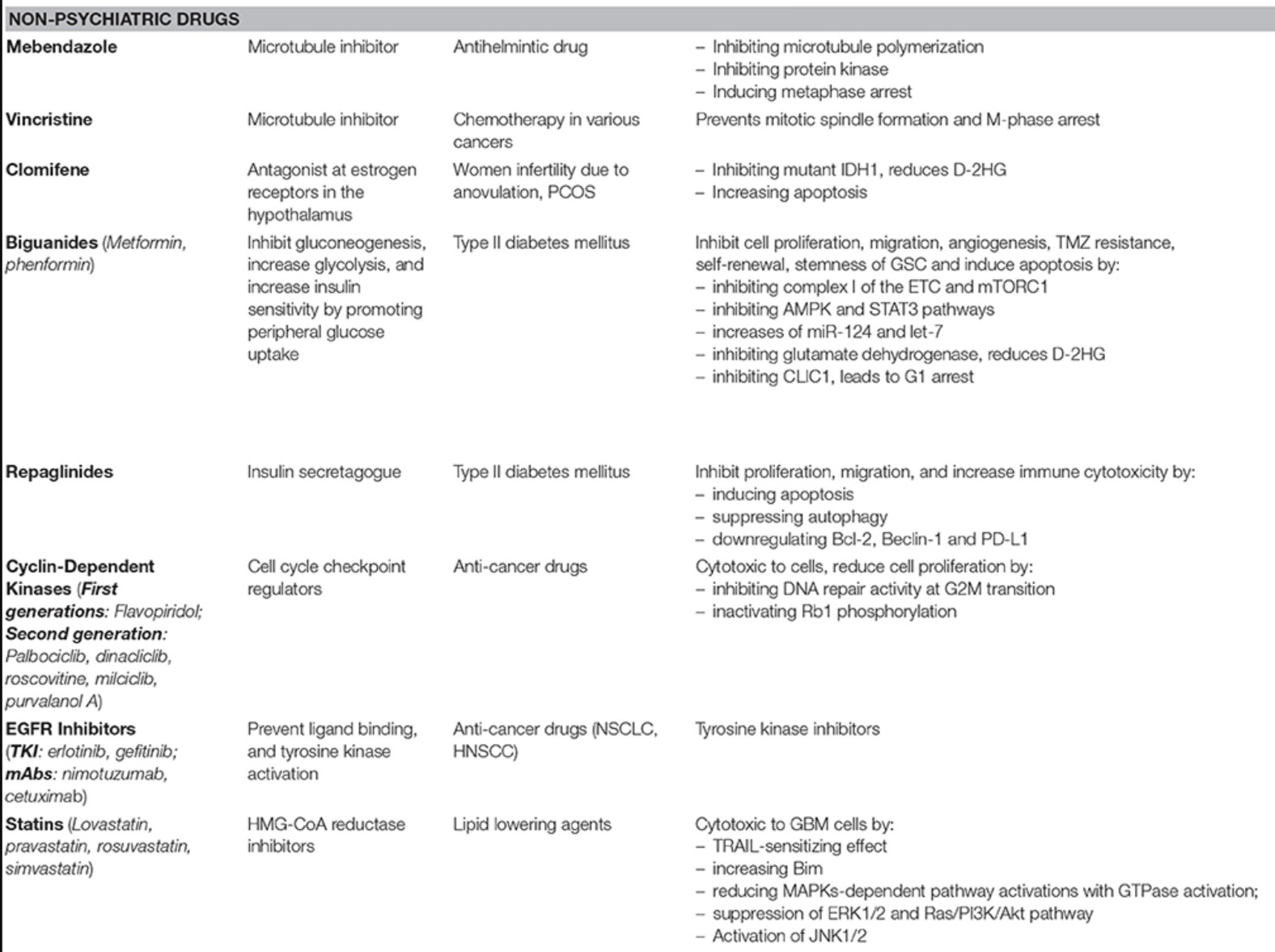
Table 1. Drug class, specific drug, and drug targets of repurposed agents currently undergoing preclinical investigation.
Drug Class Drugs Targets Reference(s)
| Antiarrhythmics | Digoxin | Na+/K+ ATPase, AKT | [19] |
| Proscillaridin A | GSK3β | [20] | |
| Antibiotics | Tetracyclines | Mitochondria | [21,22] |
| Dapsone | FPR, IL-8, Leukotriene-B4 | [23] | |
| Clofazimine | Cx46 | [24] | |
| Antidiabetics | Repaglinide | BCL-2, PD-L1, Beclin 1 | [25] |
| Antidepressants | Imipramine | ATG7 | [26] |
| Clomipramine | Complex III Cytochrome B | [27] | |
| Fluvoxamine | AKT/mTOR | [28] | |
| Sertraline | MAPK | [29] | |
| Anti-inflammatories | IP187B/Aspirin | STAT3, NF-κB, IGFR, PD-1 | [28,30,3 |
| Celecoxib | COX-2, NF-κB | 36] | |
| Ibudilast | MIF | [37] | |
| Sulfasalazine | System X(c)(-) Antiporter | [38,39] | |
| Immunosuppressants | Everolimus | mTOR, MCL-1 | [40,41,42] |
| Sirolimus | |||
| Temsirolimus | |||
| Antihypertensives | Mibefradil | NHEJ, Cav3.2 | [43] |
| Prazosin | AKT | [32] | |
| Amlodipine | PKD, Caspase 3 | [44] | |
| Pentoxifylline | NA | [45] | |
| Antipsychotics | Thioridazine | AMPK, MAP1/LC3-II, WNT | |
| DS00329 | Cyclin A, Cyclin B, Cyclin D1 | [49] | |
| Chlorpromazine | CcO Complex IV | [50,51] | |
| Fluspirilene | STAT3 | [52] | |
| Penfluridol | SOX2, OCT4, uPAR | [53] | |
| Olanzapine | AMPK | [54] | |
| Quetiapine | WNT | [55] | |
| Brexpiprazole | Survivin | [56] | |
| Antivirals | Simeprevir | PI4K | [57] |
| Ribavirin | EZH2, ERK | [58] | |
| Biologics and Small-Molecule Inhibitors | AS602801 | JNK | [59] |
| CEP-1347 | [60] | ||
| LY294002 | PI3K | [61] | |
| PX-886 | [61] | ||
| Ibrutinib | TK, BMX-STA3 | [62] | |
| Roscovitin | CDK | [63] | |
| Binimetinib | MEK | [64] | |
| Encorafenib | BRAF | [64] | |
| Disulfiram | Disulfiram | PLK1, Ubiquitin–Proteasome Pathway, AIF | [65,66,6 |
| Methylxanthines | Theophylline | PDE | |
| Theobromine | [69] | ||
| Caffeine | |||
| Neurocognitive | Riluzole | Na+ Transporter, ITAF hnRNP A1, HIF1A, AKT | [70,71,7 |
| Dimethyl fumarate | ERK1/2, AKT | [73] | |
| Idebenone | p21 | [74] | |
| Statins | Lovastatin | c-Myc, SKP2 | [75,76] |
| Simvastatin | EGFR, FGFR, c-SRC | [77] | |
| Atorvastatin | RAS | [78] | |
| Other | Aurintricarboxylic acid | NF-κB | [79] |
| Papaverine | HMGB1/RAGE | [80] | |
| Bacoside A | CAMKIIA | [81] | |
| Verteporfin | YAP, HIF1A | [82] | |
| Clomiphene | IDH1 | [83] |
Abbreviations: protein kinase B (AKT); glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3B); formyl peptide receptor (FPR); interleukin-8 (IL-8); connexin 46 (Cx46); B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2); programmed death-ligand 1 (PDL1); autophagy related 7 (ATG7); mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR); mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3); nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-KB); insulin growth factor receptor (IGFR); programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1); cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2); macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF); induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein (MCL-1); non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ); polycystin-1 (PKD); microtubule-associated protein 1A (MAP1)/1B-light chain 3 phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate (LC3-II); cytochrome c oxidase (CcO, complex IV); (sex determining region Y)-box 2 (SOX2); octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (OCT4); urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor (uPAR); AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK); phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase (PI4K); enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2); extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK); S-phase kinase protein (Skp2); epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); fibroblast growth factor receptor (EGFR); proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src (c-SRC); rat sarcoma (RAS); high-mobility group protein 1 (HMG-1); receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE); Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CAMKII); isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1).
Table 2. Drug class, specific drug, drug target, and current clinical phase of repurposed agents currently undergoing clinical investigation.
Drug ClassDrugsTargetsClinical Trial StageReferences
| Antiepileptic Drugs | Valproic Acid | HDAC | Phase II | |
| Disulfiram | Disulfiram | PLK1, Ubiquitin–Proteasome Pathway, AIF | Phase II/III | |
| Antifungals | Azoles | Hexokinase II | Phase I | |
| Clioquinol | BAX, BCL-2 | Phase I | ||
| Antimalarials | Atovaquone | STAT3 | Preclinical | |
| Chloroquine | Unclear | Preclinical | ||
| Hydroxychloroquine | LC3-II | Phase I/II | ||
| Mefloquine | NMDA | Phase I/II | ||
| Antiparasitics | Mebendazole | Microtubules, VEGF | Phase I | |
| Antihypertensives | ARBs, ACEis | Unclear | Retrospective | |
| Anti-inflammatories | Celecoxib | COX-2 | Phase I–II | |
| Immunosuppressants | Temsirolimus | mTOR, MCL-1 | Phase I | |
| Everolimus | Phase I/II | |||
| Antineoplastics | Vorinostat | HDAC | Phase I/II | |
| Cabozantinib | TK | Phase II | ||
| Arsenic Trioxide | Cytochrome C | Phase I/II | ||
| Marizomib | Proteasome | Phase I | ||
| Fimepinostat | PI3K, HDAC | Phase I | ||
| Carbonic-Anhydrase Inhibitors | Acetazolamide | CA, BCL3 | Phase I | |
| Checkpoint Inhibitors | Nivolumab | PD-1 | Phase II–III | |
| Pembrolizumab | PD-1 | Phase I–II | ||
| Ipilimumab | CTLA-4 | Phase I | ||
| Diabetic Agents | Metformin | AMPK, Cl-Channels, mTOR | Phase I/II | |
| Small Molecules and Biologics | Cetuximab | EGFR | Phase I | |
| 5-ALA | Not Applicable | Phase III | ||
| Cocktails | CUSP-9 | Survival Pathways | Phase I | |
| CLOVA | GSK-3B | Phase I | ||
| Celecoxib, Vinblastine, Cyclophosphamide | COX-2, Microtubules, DNA | Phase I |
Abbreviations: Histone deacetylase (HDAC); polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1); apoptosis inducing factor (AIF); Bcl-2-associated X protein (BAX); B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2); signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3); light chain 3 phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate (LC3-II); N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR); vascular-endothelial growth factor 2 (VEGF); cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2); mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR); myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL-1); tyrosine kinase (TK); phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K); carbonic anhydrase (CA); B-cell lymphoma 3-encoded protein (BCL-3); programmed cell death 1 (PD-1); cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA4); AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK); epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); glycogen synthase kinase (GSK) 3β; deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
************************************************************************
2018
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2018.00218/full
Drug Repositioning in Glioblastoma: A Pathway Perspective
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most malignant primary adult brain tumor. The current standard of care is surgical resection, radiation, and chemotherapy treatment, which extends life in most cases. Unfortunately, tumor recurrence is nearly universal
www.frontiersin.org
Drug Repositioning in Glioblastoma: A Pathway Perspective
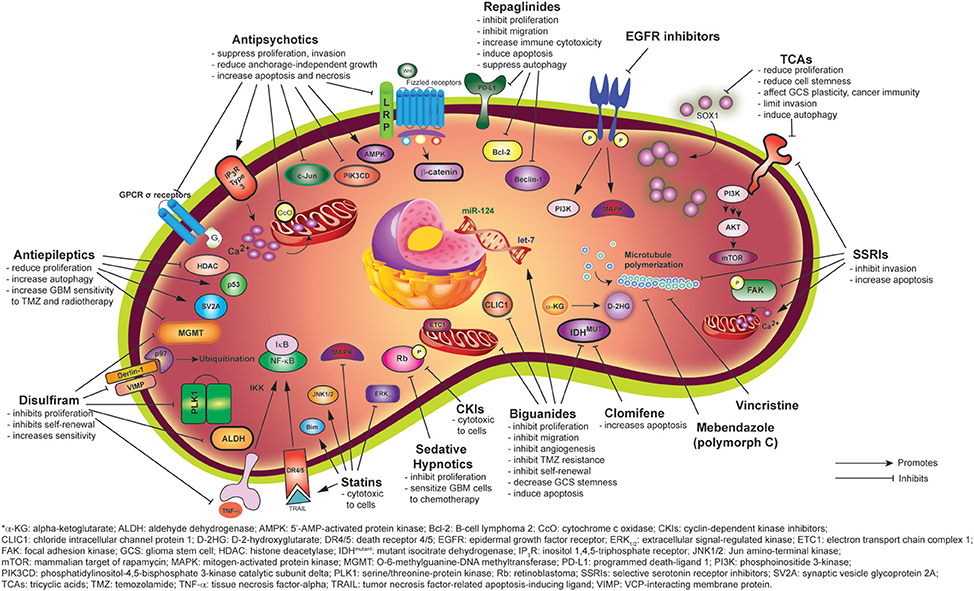
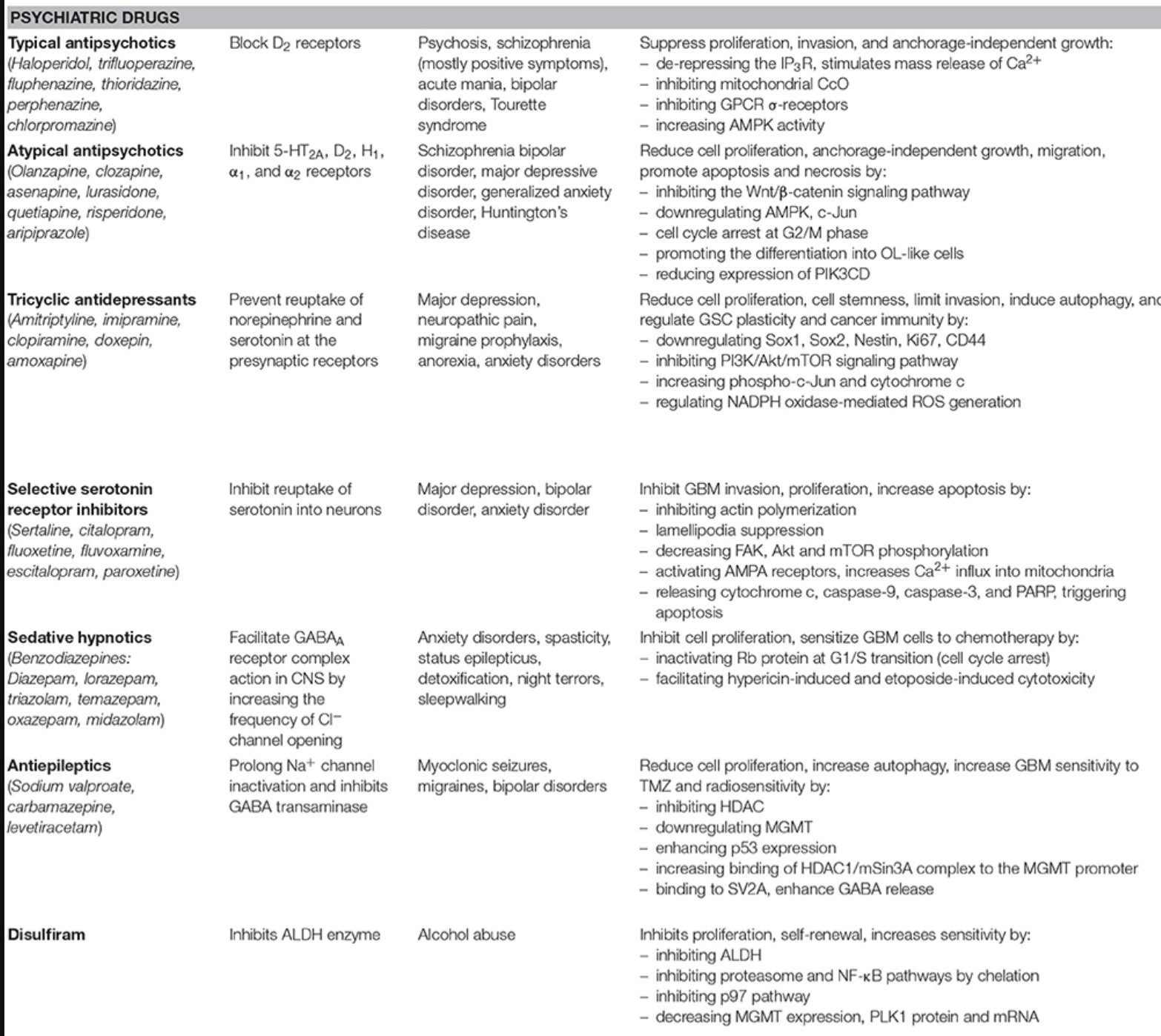

선택적 세로토닌 재흡수 억제제
일반적으로 사용되는 SSRI는 sertraline, citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, escitalopram 및 paroxetine입니다.
2010년 Caudill은 SSRI의 사용이 GBM 환자에서 안전하다고 결론지었지만 발작 위험이 더 높기 때문에 여전히 논쟁이 있습니다.
시탈로프람 및 세르트랄린과 비교하여 플루옥세틴 및 파록세틴은 CYP450 2D6 동종효소를 억제하고 GBM 환자에서 이러한 약물의 더 높은 독성을 설명할 수 있는 약물-약물 상호작용을 유발할 수 있습니다.
세포 증식을 줄이는 것 외에도 SSRI는 GBM에서 세포자멸사를 유도할 수 있습니다
플루복사민 말레산염은 50 mg/kg/day로 투여되며, 이는 일반적으로 클리닉에서 환자에게 제공되는 인간의 일일 등가 용량보다 높습니다.
플루복사민과 달리 플루옥세틴은 신경교종 세포 사멸을 유도합니다.
중요하게도, 플루옥세틴은 1차 성상교세포와 뉴런에 독성이 없습니다.
Fluoxetine은 GluR1에 직접 결합하고 AMPA 수용체를 활성화 하며 미토콘드리아로 Ca 2+ 유입을 증가시킵니다. 이 Ca 2+ 유입은 후속적으로 미토콘드리아 막 손상을 유도하고 시토크롬 c를 방출할 뿐만 아니라 카스파제-9, 카스파제-3 및 폴리(ADP-리보스) 폴리머라제(PARP)를 활성화하여 세포자멸사를 유발합니다
항간질제/항경련제
VPA는 또한 근간대성 발작, 편두통 및 양극성 장애의 치료에도 사용됩니다.
발프로산 나트륨은 Na + 채널 비활성화를 연장 하고 감마-부티르산(GABA) 트랜스아미나제를 억제하여 GABA의 농도를 증가시킵니다(표 1 ).
발프로산나트륨 또는 VPA는 또한 암 치료에서 잠재적인 보조제로 제안된 히스톤 탈아세틸화효소(HDAC) 억제제입니다.
히스톤 라이신 잔기 아세틸화 및 탈아세틸화는 후성유전학에서 가장 널리 특징지어지는 번역 후 변형 중 하나입니다.
히스톤 탈아세틸화효소는 염색질을 응축하고 종양 억제 유전자의 전사를 억제하여 신생물을 촉진하며, 이러한 HDAC는 종종 GBM에서 과발현됩니다.
후성 유전적 변형제로서 HDAC 억제제는 방사선 요법에 의해 정상 세포가 사멸되는 것을 방지하면서 암 세포의 이온화 방사선 민감도를 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
발프로산 나트륨 노출은 신경교종 세포에서 히스톤 과아세틸화를 증가시키고 세포 성장을 억제하며 세포 방사선 민감성을 증가시킵니다
그러나 VPA는 CYP2C 조효소, 에폭사이드 하이드록실라제 및 유리딘 디포스페이트-글루쿠로노실트랜스퍼라제와 같은 여러 효소를 억제할 수 있으며, 이는 바람직하지 않은 부작용과 관련될 수 있습니다.
중요하게, 일부 약물 또는 약물 조합은 면역 체계에 의한 GBM 세포의 인식에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 따라서 이러한 약물이 숙주 면역 반응을 활성화할 수도 있습니다.
HDAC 억제제로 치료할 때 GBM 세포에서도 동일한 효과가 나타납니다
일반적으로 사용되는 또 다른 항경련제인 LEV는 두개내 종양 환자에서 흔히 발생하는 국소 발작의 치료 및 예방에 효과적입니다. 그것은 소포 단백질 SV2A에 결합하고 GABA의 방출을 향상시킵니다. 또한 다른 AED에 비해 BBB에 빠르게 침투하고 치료 지수가 높습니다.
중요하게, 이 약물은 화학요법제와의 상호작용이 없기 때문에 GBM 치료에 특히 유망할 수 있습니다.
LEV는 종양 억제 단백질 p53의 발현을 향상시키고 MGMT 프로모터에 대한 HDAC1/mSin3A 복합체의 결합을 증가시킵니다
레파글리니드
레파글리니드는 1983년에 발명된 메글리티니드 계열에 속하는 비설포닐우레아 인슐린 분비촉진제입니다.
세포자멸사 유도, 자가포식 억제 또는 면역 활성화를 통한 것이라고 가정했습니다.
이는 미토콘드리아 매개 항세포자멸사 단백질 Bcl-2의 하향조절과 Beclin-1 및 PD-1/PD-L1 면역 경로의 결합을 통해 달성되는 것으로 생각되었습니다(그림 1 ).
'암치료' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 표적 DNA 손상 복구 및 반응 경로를 목적으로 하는 소분자 약물 (0) | 2021.08.22 |
|---|---|
| ⚡ 소아 뇌종양에서 암 줄기세포를 표적으로 하는 약물 용도 변경 (0) | 2021.08.22 |
| Special Supplement Formulations? (0) | 2021.08.18 |
| ⚡링크--보조 암 치료로서 천연 보충제의 조합 (0) | 2021.08.18 |
| Synergies (암 치료에 시너지효과를 일으키는 보충제들) (0) | 2021.08.18 |