2020
https://www.jcpjournal.org/journal/view.html?volume=25&number=4&spage=189
Targeting Epigenetic ‘Readers’ with Natural Compounds for Cancer Interception
Elisabetta Damiani,*, Munevver N. Duran, Nivedhitha Mohan, Praveen Rajendran,*, Roderick H. Dashwood,*. J Cancer Prev 2020;25:189-203. https://doi.org/10.15430/JCP.2020.25.4.189
www.jcpjournal.org
Targeting Epigenetic ‘Readers’ with Natural Compounds for Cancer Interception
Table 1 . Epigenetic reader modules and the histone marks recognized
ModificationResidueFamilyMember
| Acetylation | Lysine | BRD | BRD 2/3/4/T/7/9 |
| Methylation | Lysine | CRDs | MORF, MRG15 |
| Tudor domains | MBT, PHF1/19, TDRD7 | ||
| PWWP domains | BRPF1, NSD1-3 | ||
| Ankyrin repeats | GLP/G9a | ||
| Arginine | Tudor domains | WDR5, TDRD3, SMN1 | |
| Phosphorylation | Serine | 14-3-3 proteins BRCT domain | 14-3-3β/γ/η/ε/µ |
| Threonine | BIR domain | XRCC1, NBS1, BARD1 | |
| Tyrosine | PTB domain | ||
| Ubiquitination | Lysine | 53BP1 | |
| ADP-ribosylation | Glutamate | Macrodomains | RNF146 |
| Arginine | PBZ | APLF, CHFR | |
| Glutamate | WWE domain |
BRD, bromodomain; CRD, chromodomain; PWWP, Pro-Trp-Trp-Pro; MORF, monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein-related factor; MRG15, MORF4-related gene on chromosome 15; MBT, malignant brain tumor; PHF, plant homeodomain (PHD) finger; TDRD3/7, Tudor domain containing proteins 3 and 7; BRPF1, BRD and PHD finger-containing protein 1; NSD1-3, nuclear receptor binding SET domain proteins 1-3; GLP, G9a-like protein; WDR5, WD repeat domain 5; SMN1, survival of motor neuron 1; BRCT, BRCA1 C terminus; BIR, baculovirus IAP repeat; XRCC1, X-ray repair cross complementing 1; NBS1, Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1; BARD1, BRCA1 associated RING domain 1; PTB, phosphotyrosine-binding; 53BP1, tumor suppressor p53-binding protein 1; PBZ, PAR-binding zinc finger; WWE, Trp-Trp-Glu; RNF146, RING finger protein 146; APLF, aprataxin and PNKP like factor; CHFR, checkpoint with forkhead and RING finger domains (Adapted from Catia et al., 2019 [26]).
Fig. 1.
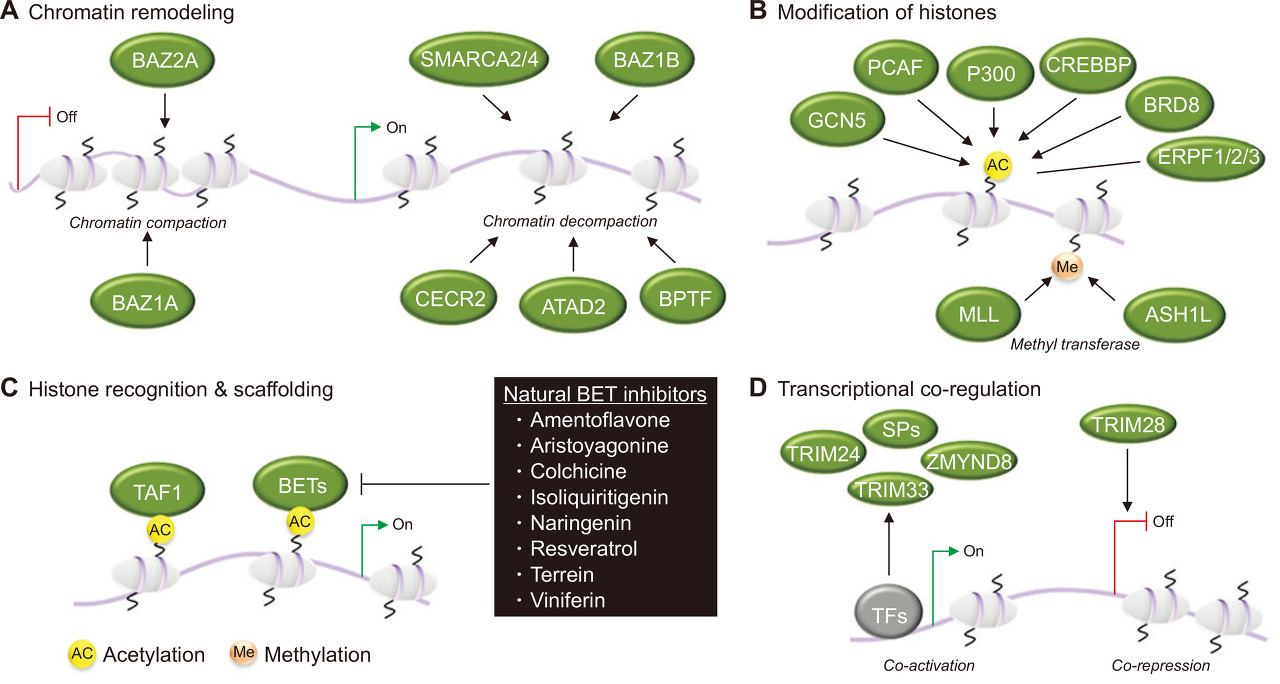
Fig. 1. Bromodomain (BRD)-containing proteins and gene regulation.
Table 2 . Natural compounds targeting epigenetic ‘reader’ domains
| Naringenin triacetate | Citrus aurantium (bitter orange) | BRD4 | 104 | |
| 3-O-acetylpinobanksin | Black poplar tree | |||
| Kaempferol tetracetate | Cudrania tricuspidata (mandarin melonberry) | |||
| Resveratrol | Peanuts, berries, grape skin, apples | BRD4 | 112 | |
| Isoliquiritigenin | Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice plant) | BRD4 | 113 | |
| Amentoflavone | Ginkgo biloba, Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort), Biophytum sensitivum, Nandina domestica (sacred bamboo) | BRD4 | 102 | |
| Fisetin | Cucumber, onion, strawberry, apple | |||
| Aristoyagonine | Sarcocapnos enneaphylla | BRD4 | 125 | |
| α-Viniferin | Caragana sinica, camphor tree, Astilbe grandis | BRD4 | 134 | |
| Euscaphic acid | Plectranthus amboinicus (French thyme, Cuban oregano, Indian mint), Ziziphus jujuba (red date) | |||
| Magnolol | Magnolia tree | BRD9 | 135 | |
| Colchicine | Colchiceine | Colchicum speciosum (autumn crocus) | BRD4 | 126 |
| Terrein | Mangrove-derived Streptomyces sp. SZ-A15 | BRD4 | 136 | |
| 4-oxo-Staurosporine | Marine-derived Streptomyces sp. NB-A22 | BRD4 | 130 | |
| 3,11α,12β,13β,6-pentahydroxy-11,12-dihydroperylen-6(13H)-one | Marine fungi: Alternaria sp. NH-F6 | BRD4 | 137 | |
| 5-hydroxymethyl-furan-2-carboxylic acid | Marine fungi: Phoma sp. CZD-F11, Aspergillus sp. CZD-F18 | BRD4 | 138 | |
| 4-hydroxymethyl catechol | Marine fungi: Phoma sp. CZD-F11, Aspergillus sp. CZD-F18 | |||
| 12-hydroxy-verruculogen TR-2 | Fumitremorgin B | Penicillium sp. DT-F29 with Bacillus sp. B31 | BRD4 | 131 |
'암치료' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 암 치료에 다양한 해양 유래 천연물의 치료적 적용 (0) | 2022.10.10 |
|---|---|
| 엑소좀 ncRNA를 조절하는 항종양 천연물 (0) | 2022.10.10 |
| 식이 파이토케미컬로 암 줄기 세포 표적화 - 약물 조합 재포지셔닝 (0) | 2022.10.10 |
| 암 예방 및 화학요법 효능에서 식이의 역할 (0) | 2022.10.09 |
| 식이 요법, 암 치료의 유망한 보조제 (0) | 2022.10.09 |