https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/11/2799/htm
Precision Nutrition and Cancer Relapse Prevention: A Systematic Literature Review
Cancer mortality rates are undergoing a global downward trend; however, metastasis and relapse after surgery and adjuvant treatments still correlate with poor prognosis and represent the most significant challenges in the treatment of this disease. Advance
www.mdpi.com
Precision Nutrition and Cancer Relapse Prevention: A Systematic Literature Review
암 재발은 유전, 전사, 환경, 내분비 신호 및 대사와 같은 많은 생물학적 상호 작용을 포함합니다.
이러한 상호작용은 암 재발 및 전이를 이해하는 데 또 다른 복잡성을 추가하여 치료 기회의 진행을 지연 시킵니다.
폐암과 백혈병 사망률은 유방암, 결장암, 전립선에 비해 재발률이 높기 때문이며, 종양의 수술적 절제와 보조적 치료가 더 높은 생존율을 달성합니다.
재발을 예방하고 치료하는 치료법을 개발하기 위해서는 유전자 발현과 재발의 연관성을 발견하는 것이 가장 중요합니다.
예를 들어, 긴 비암호화 RNA AWPPH 과발현이 TGF-b1의 상향 조절에 의해 NSCLC 재발에 관여하여 최종적으로 암 세포 이동 및 침습을 증가시키는 것으로 최근에 확인되었다.
환자가 획득한 많은 수의 재발 특이적 돌연변이는 다른 기능에 관여하는 유전자에 영향을 미치고, 이는 클론 진화를 유도하고 화학요법 내성을 초래하므로 이 과정의 높은 분자적 복잡성을 나타 냅니다 .
재발-특이 돌연변이의 역할을 이해하면 고위험 환자의 치료를 위한 새로운 치료법의 개발이 촉진될 것입니다.
본질적으로, 약물 내성 및 전이 및 재발과 관련된 이전에 알려지지 않은 분자 메커니즘과 관련된 최근의 발견은 대체 치료 전략을 요구하며, 그 중 대사가 새로운 암 치료 지원으로 나타날 수 있습니다.
암 재발은 다수의 유전적 돌연변이와 생화학적 과정으로 인해 발생하지만 유전체학, 대사체학 및 단백질체학의 발전으로 유전학 및 미생물군집 변이로 인한 대사 다양성과 정밀 의학을 제공하는 종양의 상세한 분류로 인한 대사 다양성에 대한 더 나은 이해가 가능합니다. 마찬가지로, 대사 변이를 가장 잘 이해하면 영양소, 대사, 미생물군 및 관련 유전자 간의 상호 작용을 알 수 있습니다.29 ].
정밀 영양 및 암 치료
수년에 걸쳐 예방적 접근에서 또는 특정 식품의 소비를 종양 생성 및 성장과 연관시킴으로써 식이요법을 암과 연관시키기 위해 수많은 역학 연구가 수행되었습니다.
의학의 정밀 요법 개발과 병행하여 정밀 영양은 유전 및 후성 유전적 변이 및 미생물군집과 같은 잘 확립된 요인에 의존하는 신흥 과학입니다 .
최근에 다양한 생리활성 식품으로 인간 세포주를 처리하는 것이 다른 유전자의 발현에 영향을 미치는 능력에 따라 생리학적 속성에 영향을 미친다는 것이 밝혀졌습니다
암에 대한 영양 요법을 보완 의학으로 사용할 수 있는 가능성은 독성이 적고 환자가 더 잘 받아들일 수 있다는 장점으로 인해 국제적으로 받아 들여지고 있습니다.
역학 연구는 정밀 영양의 맥락에 진입하여 식물 요법의 효과를 크게 향상시킨 분자 메커니즘 측면에서 추가 연구를 촉발했습니다[
매우 구체적인 치료 목표에 도달해야 하기 때문에 정밀 영양은 증식, 침습, 혈관 신생 및 전이 또는 세포 사멸과 관련된 유전자 발현 조절 및 신호 전달 경로 측면에서 분자 수준에서 잘 확립된 작용 기전을 가진 개별 식품을 기반으로 해야 합니다.
예를 들어, 증식 신호를 억제하고 발암성 대사를 약화시키며 염증을 차단하는 영양 전략을 통해 암과 관련된 유전적 불안정성을 공격하는 것이 가능하다는 것이 밝혀졌습니다.
폴리페놀 외에도 커큐민(디페룰로일메탄)은 암, 특히 백혈병에 대한 잠재적인 치료제로 최근 몇 년 동안 가장 많이 연구된 식품 중 하나입니다.
로즈마리 추출물과 같은 전통 식품은 효과와 관련된 분자 메커니즘 및 현재 사용되는 항암제와의 상호 작용을 식별하여 암 치료에서 정밀 영양 보충제의 잠재적 성분으로 제안되었습니다.
결장직장암의 경우 지질 대사 관련 유전자는 원발성 종양과 원위부 전이 모두에서 광범위한 종양 형성 단계가 지질 대사에 의해 영향을 받을 수 있기 때문에 정밀 영양 요법에 대한 관련 관심을 얻었습니다.
마지막으로, 식품 성분의 다중 표적화 프로파일은 특정 유전자 발현 또는 신호 전달 경로의 조절을 통해 항암 분자 메커니즘을 유발하는 잠재적 역할에 대해 조사되고 있습니다.
표 2의 모든 화합물은 안전성과 생리활성이 광범위하게 연구된 자주 사용되는 식품이다.
전반적으로, 이러한 제품은 세포 증식, 이동 또는 침입과 관련된 경로에 영향을 미치거나 세포자멸사를 활성화함으로써 화학요법 치료와 시너지 효과를 냅니다.
전체적으로 이러한 효과는 종양 성장 억제를 초래하여 최종적으로 암 완화 및 재발 예방에 기여합니다.
식품 추출물의 항암 효과에 대한 연구와 관련하여 각 추출물에 여러 화합물이 통합되어 있기 때문에 작용 메커니즘에 대한 지식은 폴리페놀 식품에 비해 훨씬 제한적입니다.
그럼에도 불구하고, 이들은 다양한 암 치료를 위한 영양 보충제의 성분을 잠정적으로 구성할 수 있기 때문에 본 연구에서 고려되었습니다.
표 3 은 이 리뷰에 포함된 알려진 분자 메커니즘을 가진 식품 추출물의 항암 효과와 특징을 요약한 것입니다.
Table 2. 폴리페놀 식품과 관련된 포함된 연구의 특성.
결과는 생물 활성 식품에 따라 알파벳순으로 정렬됩니다.
유전자 발현, 신호 전달 경로, 단백질 안정성 또는 단백질 번역 후 변형과 관련하여 억제(↓) 또는 활성화(↑)를 나타내는 분자 메커니즘이 요약되어 있습니다.
조절 대상은 기울임꼴로 표시됩니다.
Bioactive Foodstuff Source Cancer Type Molecular Mechanism Anticancer Effect
| Apigenin | Fruits Vegetables Food herbs |
Prostate | Apoptosis ↓ Bcl-2, sharpin and survivin ↑ caspase-8, Apaf-1, p21, p53 Signaling pathways inhibition ↓ PI3K/Akt, NF-κB Cell cycle inhibition ↑ p21, CDK-2, -4, -6 Migration inhibition ↓ Snail |
Apigenin synergizes with cisplatin significantly increasing its effects on prostate cancer stem cells (CSCs) | [57] |
| Apigenin | Fruits Vegetables Food herbs |
Lung | Migration/invasion inhibition ↓ CD26/DPPIV ↓ Akt, Snail/Slug EMT Cell growth and metastasis inhibition ↓ CD26 |
CD26high/Akthigh Tumors show the shortest recurrence times of non-small cell lung cancer. apigenin inhibits the migration/invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting CD26 |
[58] |
| Curcumin | Turmeric | Prostate | Apoptosis ↓ Bcl-xl, NF-κB Virus infection increase ↓ STAT1 |
Curcumin synergizes with vesicular stomatitis virus modulating antiviral responses and potentiating components of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. | [59] |
| Curcumin | Turmeric | Colorectal | Gene expression regulation in pathways related with DNA replication, cell cycle, protein export, glutathione metabolism and porphyrin metabolism HSPA5, SEC61B, G6PD, HMOX1, PDE3B |
Cooperative mechanisms of action of curcumin and oligomeric proanthocyanidins show enhanced anti-tumoral properties, opening up new effective therapies. | [60] |
| Curcumin | Turmeric | Breast | Cell proliferation, migration, invasion suppression ↑ E-cadherin ↓ Vimentin, Fibronectin, β-catenin Decreased stem cell features ↓ Oct4, Nanog, Sox2 |
Anti-metastasis activity of curcumin via the inhibition stem cell-like features and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. |
[61] |
| Curcumin | Turmeric | Lung | Downregulated EGFR activity (growth inhibition) ↓ Sp1-HADC1 interaction Signaling pathways inhibition ↓ RTKs, ERK/MEK, AKT/S6K Autophagy induction |
Combination of curcumin and gefitinib sensitizes EGFR-TKI resistance in wild-type EGFR and/or KRAS mutant cell lines promoting autophagy -mediated cell apoptosis. | [62] |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | Fish or algae oils | Colorectal | Induced expression of genes related to apoptosis. Proteasome inhibition in favor of proapoptotic proteins resulting in an accumulation of tumor-suppressor proteins and induction of apoptosis. | DHA have chemopreventive effect significantly inhibiting the growth of cancer cells. | [63] |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | Fish or algae oils | Colorectal | Inhibition of 5-FU-induced IL-1β secretion, caspase-1 activity, JNK activation | DHA enriched diet reduces circulating IL-1β concentration and recurrence in 5-FU-treated tumors | [64] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) | Green tea | Lung | Apoptosis ↑ GADD153, death receptor 5, and p21waf1 Protein acetylation inhibition ↓ HDAC4, -5, -6 |
In combination with the synthetic retinoid Am80, EGCG or HDAC inhibitor celecoxib, enhances cell apoptosis and increases drug sensitivity in resistant cells. | [65] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) | Green tea | Lung | CSCs growth inhibition and apoptosis ↑ has-mir-485-5p ↓ RXRα |
EGCG inhibits non–small-cell lung cancer cell growth and induces cell-apoptosis. | [66] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) | Green tea | Breast | Bioinformatic prediction: disruption of signaling proteins involved in cell death and survival, DNA replication, recombination and repair; and cell cycle JUN, FADD, NFKB1, Bcl-2, GNAO1, MMP14 |
EGCG is predicted to affect several molecular pathways that appear altered in breast cancer. | [67] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) | Green tea | Colorectal | Apoptosis and DNA damage ↓ GRP78, MDR1 ↑ NF-κB, miR-155-5p |
EGCG acts as a chemo-sensitizer to 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer cell lines. | [68] |
| Naringenin | Citrus fruits | Prostate | Apoptosis ↑ PI3K/AKT ↓ ERK1/2, p38, JNK Loss of MMP ROS generation Loss of mitochondrial membrane potential |
Naringenin suppresses cell proliferation and migration, and induces apoptosis and ROS production. In combination with paclitaxel, enhances cell proliferation inhibition effects. | [69] |
| Procyanidin B2 3,3″-di-O-gallate (B2G2) | Grape seed | Prostate | CSCs cell renewal ↓ Cleaved Notch1, HES-1, NF-κB, STAT3. |
B2G2 targets both differentiated cells and CSCs in the tumor mass and impairs prostate cancer growth and relapse | [70] |
| Quercetin | Fruits Vegetables Red wine |
Prostate | Cell proliferation inhibition ↓ PI3K, AKT, ERK1/2, p38, ABCG2, NF-κB Inhibition of migration in PC3 and CD44+/CD133+ ↓ PI3K/PTEN, MAPK, NF-κB |
Downmodulation of growth factor midkine (MK) expression curbs migration, tumorigenesis and progression of CD44+/CD133+ and prostate cancer cells. Quercetin enhances MK inhibition, promoting apoptosis and effectively eliminating cancer cells. | [71] |
| Quercetin | Fruits Vegetables Red wine |
Breast | Cell proliferation inhibition ↓ mTOR, PI3K, Akt, CyclinD, Bcl-2 Cell viability inhibition ↓ ERα |
Quercetin inhibits PI3K/Akt/mTOR-signaling, decreasing proliferation in CD44+/CD24− CSCs, thereby decreasing breast CSC population. | [72] |
| Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG) | Flaxseed | Breast | Inhibition of tumor growth and macrophage infiltration Cell survival inhibition ↓ p65 and NF-κB |
SDG treatment, and in particular its metabolite enterolactone, correlates with restrained breast tumor growth in ERα-negative breast cancer. Therefore, SDS could be effective as an adjuvant treatment to reduce recurrence. | [73] |
| β-Sitosterol-d-glucoside (β-SDG) |
Sweet potato | Breast | Activation of tumor supressors ↑ miR-10a Cell signaling regulation ↓ PI3K/Akt, Bcl-2 Apoptosis ↑ caspase proteases |
Inhibitory effects of β-SDG breast-cancer cell growth. Promising therapeutic agent for treating breast cancer. | [74] |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table 3. 생리 활성 천연 추출물과 관련된 포함된 연구의 특성
Extract Source Bioactive Fraction Cancer Type Molecular Mechanism Anticancer Effect
| Andrographis paniculata |
Andrographolide | Prostate | Apoptosis Cell cycle and DNA repair modulation ATM, BLM, BRCA2, BRIP1, CLSPN, NBN, PALB |
Andrographolide promotes DNA damage in tumor cells leading to cell death. | [75] |
| Aronia | 3-O-p-Coumaroyltormentic Acid | Breast | Cell proliferation inhibition Reduction of cancer cell subpopulations CD44high/CD24low, ALDH+ Self-renewal inhibition ↓ CD44, Sox2, Oct4 Cell survival inhibition ↓ c-Myc |
Promotes CSCs cell death inhibiting survival and self-renewal potential. |
[76] |
| Castor oil | ω-hydroxyundec-9-enoic (ω-HUA) | Breast | Increased apoptosis and ROS generation ↑ Caspase-3, PARP, p38, JNK |
ω-HUA-induced cell death promotes tumor regression. |
[77] |
| Ginger | Gingerols | Leukemia | Antiproliferative impact on methotrexate-resistant tumor cell lines not by modifying the expression levels of the ABCA2 and ABCA3 drug efflux genes. |
Antitumor impact of ginger in combination with methotrexate on T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). |
[78] |
| Ginseng | Ginsenoside Rg3 | Colorectal | Cell survival inhibition ↓ NF-κB, Cyclin D1, Survivin, Cox-2, VEGF |
Rg3 enhances radiotherapy by impairing cell survival, finally inhibiting tumor growth. |
[79] |
| Grape seed extract | Monomeric, dimeric and trimeric proantho-cyanidins (OPCs) |
Colorectal | Cell cycle and DNA replication inhibition ↓ CCNE2, E2F1 ↑ SFN, CDKN1A, MAD1L1 Cell migration inhibition ↓ MMP2, EZH2, WNT5A Upregulation tumor suppressor gene PTEN |
OPCc block various oncogenic pathways and inhibit colorectal cancer growth through multiple cell pathways. |
[80] |
| Isodon | Flexicaulin A | Colorectal | Cell proliferation inhibition ↑p21 |
Flexicaulin A inhibits cancer cell proliferation, emerging as a promising support treatment in colorectal malignancies. |
[81] |
| Orange peel | Nobiletin Sinensetin Sutellarein tetramethylether Tangeretin |
Colorectal | Cell proliferation inhibition Cancer stemness and self-renewal inhibition ↓PROM1, LGR5 EMT transition modulation ↑CDH1 ↓ZEB1, SNAI1 |
Orange peel extract reduces cell proliferation and modulating cancer stemness and self-renewal. Synergistical interaction with 5-fluorouracil. |
[82] |
| Sorghum | Phenolic acids and flavonoids |
Prostate | Apoptosis ↓ Bcl-2, Akt ↑ Bax Cell cycle arrest ↓ Cyclin D1, Cyclin E ↑ p21Waf/Cip1 |
Donganme sorghum ethyl- acetate extract (DSEE) suppresses cell proliferation by activating apoptosis. |
[83] |
| Rosemary and shark liver oil rich in alkylglycerols |
Phenolic diterpenes |
Colorectal | Modulation of expression of genes involved in immune-modulation, inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid metabolism, and tumorigenesis. |
Activation of innate immune, cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory responses towards effector cells. Gene expression modulation supports its potential usefulness in cancer patients. |
[84] |
| Thunder god vine | Triptolide | Breast | Cell proliferation inhibition Caspase-3-mediated apoptosis Autophagy induction |
Triptolide could be an efficient anticancer agent specific for triple negative breast cancers. |
[85] |
| Watercress and broccoli extracts | Phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) and sulforaphane (SFN) |
Colorectal | Impaired cell proliferation Decreased cell self-renewal Decreased cell adhesion ↓ E-cadherin Reversion of CSC ALDH1-mediated chemoresistance ↓ LGR5, PROM1, ALDH1 CSC proliferation Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2 |
Chemotherapeutic potential of ITC-enriched extracts in CRC therapy by targeting critical aspects of tumor progression and tumor relapse. |
[86] |
Table 4. Curcumin nano-formulations.
Bioactive FoodstuffCancer TypeNano-Formulation Molecular Mechanisms Anticancer Effect
| Curcumin | Breast | H-ferritin (HFn) nanoparticle | HFn biopolymer specifically binds to the TfR1 receptor, found to be overexpressed in triple negative breast cancer cells. | HFn nanoparticles raises solubility, stability and bioavailability of curcumin, potentiating its effects as a doxorubicin sensitizer. | [87] |
| Curcumin | Breast | Fe3+-curcumin and Cu2+-curcumin complexes encapsulated into poly(styrene)-co-maleic acid (SMA) micelles. | Metal complexes prevent curcumin degradation. Its sequential encapsulation into SMA micelles improves their solubility and stability and their accumulation in tumors. | Improved chemical stability and tumor growth reduction. Higher stability in biological fluids. Increased ability to enter and accumulate in tumor cells. | [88] |
| Curcumin | Prostate | Dextran nanobubbles | Effective internalization into tumor cells and sustained release of curcumin, enhancing curcumin potential to inhibit cell migration and promote apoptosis. | Lower doses of curcumin are needed to get the same anti-cancer effects. Helping to prevent metastasis and relapse. | [89] |
| Curcumin in combination paclitaxel | Breast | Hyaluronic acid (HA) lipoid hybrid nanoparticles | HA interacts with the CD44 receptor, overexpressed in breast CSCs. | Enhanced anti-tumor impact by inhibiting cell growth and migration. | [90] |
| Curcumin in combination paclitaxel | Breast | Poly (ethylene glycol)-benzoic imine-poly(g-benzyl-L-aspartate)-b-poly(1-vinylimidazole) block copolymer | This pH polymer can switch its surface charge in order to facilitate their intake by tumor cells, solving issues regarding drug delivery into inner regions of solid tumors. | The formulation increases the extent of action of the curcumin-paclitaxel combination. | [91] |
영양 전략의 통합은 치료 효과를 높이고 암 재발을 예방하기 위해 보조 요법으로 치료받는 환자에게 특히 중요할 수 있습니다.
몇 가지 생리활성 식품의 작용 기전에 관한 지식과 대부분이 잘 확립된 분자 표적을 다룬다는 사실은 잠재적인 임상 사용으로의 전환을 가능하게 합니다.
지난 10년 동안 생리 활성 천연 제품의 항암 효과를 조사하는 연구가 증가했습니다. 그러나 영양소가 재발을 예방할 수 있는 분자 메커니즘이 연구된 것은 아주 최근에야 이루어졌습니다.
표 2 는 문헌 검토에서 확인된 생리활성 식품 화합물의 목록과 항암 효과의 분자 메커니즘을 포함합니다.
폴리페놀은 다양한 생물학적 활성으로 인해 수십 년 동안 가장 많이 연구된 화합물 계열입니다.
또한, 일부 플라보노이드는 최근 재발 방지 치료에 유용할 수 있는 항종양 및 항증식 활성을 나타냈습니다.
녹차에 존재하는 플라보노이드인 에피갈로카테킨-갈레이트(EGCG)는 종양 세포 성장을 억제하고 세포자멸사를 증가시켜 종양 억제를 촉진하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
이 화합물은 인간 대장암 세포를 5-플루오로우라실에 민감하게 하여 보조 치료 효과를 높이고 예후를 개선하며 최종적으로 종양 재발 위험을 감소시킵니다.
EGCG는 또한 hsa-mir-485-5p/RXRα 축의 조절을 통해 암 줄기 세포 유사 성장을 차단하고 폐암 세포에서 단백질 아세틸화를 하향 조절함으로써 폐암 마우스 이종이식에서 폐암 재발을 예방할 수 있습니다
EGCG는 또한 세포 사멸 및 생존과 관련된 여러 경로에 영향을 미쳐 잠재적으로 암 진행을 감소시킬 것으로 예측되었습니다.
그러나 이러한 의미에서 추가 분자 검증이 필요합니다.
재발 예방을 위한 흥미로운 기능을 가진 또 다른 플라보노이드는 양파와 같은 야채에 존재하는 케르세틴입니다.
케르세틴은 전립선 암 줄기세포를 효과적으로 제거하는 PI3K/Akt 또는 NF-κB와 같은 중요한 신호 표적을 조절하여 세포 사멸을 촉진하고 세포 증식을 억제합니다.
또한 MK의 하향 조절에 의해 전립선암 세포주의 세포 이동 능력과 진행을 제한합니다.
유방암에서 케르세틴은 mTOR, PI3K 및 Akt 단백질의 발현 및 활성화 수준을 감소시켜 MCF7 암세포 증식을 현저하게 억제함으로써 재발을 예방하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다..
정밀 영양 제품 개발에 잠재적으로 흥미로운 효과가 있는 또 다른 플라보노이드는 과일, 채소 및 파슬리와 같은 식용 허브에 존재하는 아피제닌입니다.
이 화합물은 전립선암 줄기세포에 대한 세포독성과 항이동 효과를 모두 향상시키는 시스플라틴 보조 요법의 효과를 향상시킵니다.
Apigenin은 또한 세포 이동 및 침입을 억제하여 비소세포성 폐암 세포주 및 생체 내 동소성 생물발광 이종이식 모델에서 전이 및 재발을 예방하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
다른 흥미로운 플라보노이드는 감귤 껍질에서 추출한 나린제닌으로 전립선암 세포의 증식을 억제하고 세포자멸사를 유도하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
그리고 포도씨에서 추출한 프로시아니딘-B2-3,3"-디-O-갈레이트(B2G2)는 분화된 세포와 암 줄기세포를 모두 표적으로 삼아 종양 질량 감소를 유도합니다.
커큐민은 이전의 수많은 연구의 주제였던 또 다른 생리 활성 식품입니다.
Bcl-xl 및 NF-κB와 같은 중요한 항-세포자멸사 이펙터를 조절하는 능력으로 인해 항암 효과는 잠재적인 재발 예방 치료에서 두드러진 관심을 받고 있습니다.
또한, 커큐민은 항바이러스 반응을 조절하는 수포성 구내염 바이러스(VSV) 기반 종양 용해 치료 및 전립선암 세포 모델에서 내재적 세포자멸사 경로의 구성요소와 상승 작용을 합니다.
또한, 결장직장암에서 커큐민은 HSPA5 , SEC61B , G6PD , HMOX1 및 PDE3B의 유전자 발현을 조절할 수 있습니다.,
DNA 복제 또는 세포 주기와 같은 필수 경로에 영향을 미칩니다. 한편,
커큐민과 올리고머 프로안토시아니딘의 시너지 효과는 두 화합물이 유사한 분자 메커니즘을 공유하기 때문에 효과적인 치료법을 개발할 수 있는 기회로 떠오르고 있습니다.
최근 유방암 세포 모델에서 커큐민의 관련 효과가 발견되었는데, 이 화합물은 E-cadherin의 발현을 증가시키고 중간엽 마커의 발현을 감소시킬 수 있다는 것입니다.
또한 커큐민은 EGFR 억제제인 게피티닙(gefitinib)과 같은 암에 사용되는 일부 표적 약물의 효과를 향상시켜 자가포식 매개 세포자멸사를 유도하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
이 관찰은 암 재발을 예방하기 위한 치료와 함께 이 화합물을 사용할 수 있는 기회를 열어줍니다.
일부 지질 특성 식품 생리 활성 물질은 또한 암 재발 예방에 흥미로운 작용 기전으로 항암 효과를 나타냅니다.
이러한 의미에서 도코사헥사엔산(DHA)은 대장암 세포의 성장을 조절하고 세포자멸사와 관련된 유전자의 발현을 유도합니다.
또한 β-sitosterol- d -glucoside 는 유방암 세포의 성장을 억제하는 효과가 있습니다.
인용된 기사는 진저롤이 풍부한 생강 추출물의 효과를 분석하여 이 추출물이 약물 내성 백혈병 하위 라인에서 높은 항증식 효과와 함께 메토트렉세이트와 시너지 상호작용을 발휘함을 보여줍니다.
그럼에도 불구하고 이 효과를 지원하는 메커니즘은 설명되지 않습니다. 실제로 최근에 연구된 다른 식품 추출물에서도 동일한 일이 발생하며 추가 연구가 필요할 것입니다.
표 3 은 참고문헌 조사에서 확인된 천연 추출물에 대한 출판물을 보여줍니다.
일반적으로 흥미로운 항종양, 항증식 또는 항전이 효과가 입증되지만 이러한 효과와 관련된 분자 메커니즘은 대부분의 경우 거의 알려지지 않은 상태로 남아 있습니다.
예외적으로 포도씨 추출물은 세포 주기와 이동을 조절함으로써 결장직장암의 항종양 효과와 관련된 프로안토시아니딘이 풍부한 커큐민과 조합될 수 있습니다.
결장직장암에서 세포 성장, 종양 진행 및 전이에 대한 효과가 확인된 다른 추출물은 페네틸 이소티오시아네이트가 풍부한 물냉이 추출물; 진세노사이드 Rg3가 풍부한 인삼 추출물 ; 플렉시컬린 A가 풍부한 이소돈 추출물입니다.
중요하게도, 노비레틴, 시넨세틴, 스쿠텔라레인 테트라메틸에테르 및 탄게레틴이 풍부한 오렌지 껍질 추출물은 결장직장암에서 5-플루오로우라실과 상승적인 상호작용을 발휘하여 EMT 전환을 조절하고 세포 증식을 억제하고 암 줄기세포를 조절하여 이 조합의 재발 예방 요법에서 상당한 잠재적 사용을 보여줍니다
추출물들의 낮은 독성으로 인해 영양 보충제로 다른 지원 요법에 적합합니다.
암 치료에 생리활성 식물화학 식품을 적용할 때 극복해야 할 장벽 중 하나는 이러한 제품의 생체이용률이 자주 부족하다는 것입니다.
흥미롭게도, 로즈마리 추출물의 생리 활성 지질 매개체로 알킬글리세롤이 풍부한 상어 간유를 사용하면 대장암에서 면역 조절, 염증, 산화 스트레스, 지질 대사 및 종양 형성과 관련된 유전자의 발현에 시너지 효과가 나타난다고 보고되었습니다.
이 외에도 불용성 및 불안정한 제품의 좋은 예는 커큐민입니다.
이 화합물은 종양 성장과 암 재발을 조절하는 수많은 신호 및 분자 경로에 작용하는 강력한 효과기로 부상하고 있습니다. 커큐민의 특성에 대한 지식이 증가하고 있음에도 불구하고, 커큐민은 생체이용률 및 안정성 측면에서 한계로 인해 치료 화합물로 승인될 수 없습니다. 이와 관련하여 여러 제제 연구가 수행되고 있으며 상당수의 사례에서 개별 생리 활성 물질보다 더 나은 치료 결과를 제공했습니다
결론
암 연구의 맥락에서 보조 치료에 생리 활성 식품의 사용을 기반으로 하는 영양 요법을 언급하는 연구는 여전히 제한적이지만, 종양 성장, 진행, 종양 성장, 진행, 종양 성장의 조절 효과가 입증된 몇 가지 식물화학적 생리 활성 식품이 있기 때문에 현재 결과는 고무적입니다.
암 재발 치료에 적용할 경우 적절한 성공 확률로 사람을 대상으로 테스트할 수 있습니다( 그림 2).
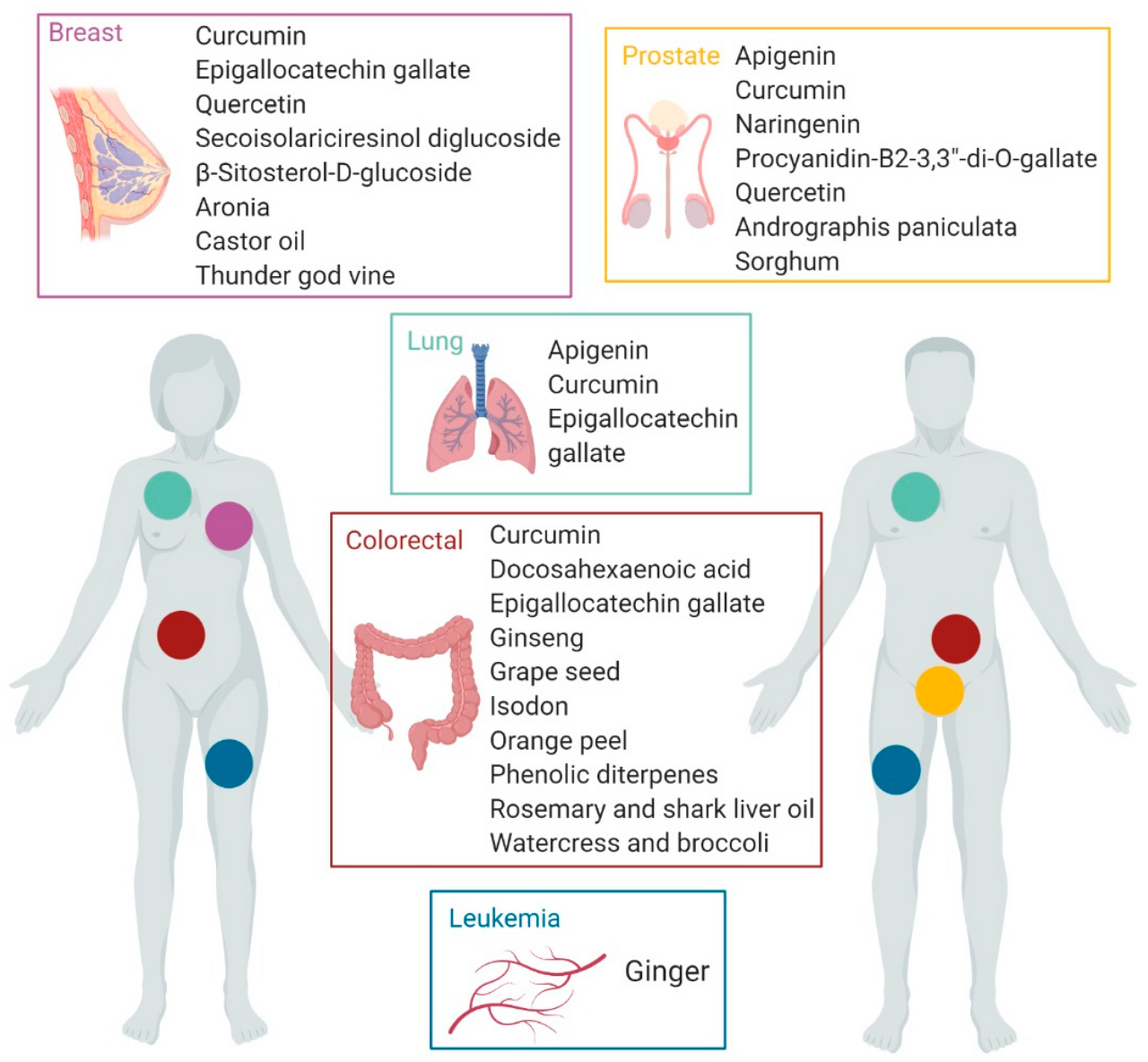
그림 2. 암 치료에 효과가 입증된 생리활성 식품 및 천연 추출물.
암 이질성은 이 질병의 치료를 특히 어렵게 만드는 이 질병의 특징 중 하나입니다.
다양한 유형의 암 치료에서 여러 생리활성 식품의 메커니즘에 관한 연구의 증가는 정밀 암 치료의 새로운 지평을 열었습니다.
종양 성장 및 전이를 억제하는 특정 유전자 표적 또는 다른 분자 경로와의 연관성은 중요한 맞춤 구성 요소를 구성합니다.
또한, 여러 화학 요법 약물과 높은 시너지 효과를 보여 이러한 항종양 효과의 증강제 역할을 하거나 화학 요법 내성을 민감하게 하고 되돌립니다.
종양 성장 및 전이를 억제하는 특정 유전자 표적 또는 다른 분자 경로와의 연관성은 중요한 맞춤 구성 요소를 구성합니다. 또한, 여러 화학 요법 약물과 높은 시너지 효과를 보여 이러한 항종양 효과의 증강제 역할을 하거나 화학 요법 내성을 민감하게 하고 되돌립니다.
이러한 제품은 암성 과정의 치료에서 재발 방지를 다루는 정밀 영양 요법에 유용할 수 있는 새로운 보완제로 부상하고 있습니다.
'대사' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 유방암에서 치료 표적으로서의 지방산 합성효소(FASN) (0) | 2021.09.12 |
|---|---|
| 암에서 지방산 대사의 확장된 역할 (0) | 2021.09.12 |
| 종양 미세환경의 대사 조절제로서의 천연 화합물 (0) | 2021.09.12 |
| 포도당 이용 및 지질 합성을 차단하는 파이토케미컬 (0) | 2021.09.12 |
| 암 치료를 위한 암 대사 표적의 새로운 역할 (0) | 2021.09.10 |